Meiotic recombination hotspots: shaping the genome and insights into hypervariable minisatellite DNA change
- PMID: 9352183
- PMCID: PMC3151733
- DOI: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60171-4
Meiotic recombination hotspots: shaping the genome and insights into hypervariable minisatellite DNA change
Abstract
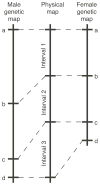
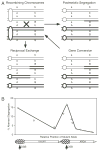
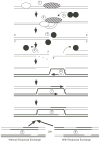
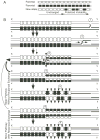
Meiotic homologous recombination serves three principal roles. First, recombination reassorts the linkages between newly-arising alleles to provide genetic diversity upon which natural selection can act. Second, recombination is used to repair certain types of DNA damage to provide a mechanism of genomic homeostasis. Third, with few exceptions homologous recombination is required for the appropriate segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Recombination rates are elevated near DNA sites called "recombination hotspots." These sites influence the distribution of recombination along chromosomes and the timing of recombination during the life cycle. Recent advances have revealed biochemical steps of hotspot activation and have suggested that hotspots may regulate when and where recombination occurs. Two models for hotspot activation, one in which hotspots act early in the recombination pathway and one in which hotspots act late in the recombination pathway, are presented. The latter model can account for changes at hypervariable minisatellite DNA in metazoan genomes by invoking resolution of Holliday junctions at minisatellite DNA repeats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of CSM3, MRC1, and TOF1 in minisatellite stability and large loop DNA repair during meiosis in yeast.Fungal Genet Biol. 2013 Jan;50:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Nov 17. Fungal Genet Biol. 2013. PMID: 23165348 Free PMC article.
-
Human minisatellites, repeat DNA instability and meiotic recombination.Electrophoresis. 1999 Jun;20(8):1665-75. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(19990101)20:8<1665::AID-ELPS1665>3.0.CO;2-L. Electrophoresis. 1999. PMID: 10435430 Review.
-
Trans-regulation of mouse meiotic recombination hotspots by Rcr1.PLoS Biol. 2009 Feb 17;7(2):e36. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000036. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19226189 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination hotspots - a comparative view.Plant J. 2015 Jul;83(1):52-61. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12870. Epub 2015 May 20. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 25925869 Review.
-
LDsplit: screening for cis-regulatory motifs stimulating meiotic recombination hotspots by analysis of DNA sequence polymorphisms.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Feb 17;15:48. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-48. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24533858 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the Mts1-Mts2-dependent ade6-M26 meiotic recombination hot spot and developmental decisions by the Spc1 mitogen-activated protein kinase of fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Dec;18(12):7575-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.12.7575. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9819443 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution patterns of meiotic recombination across the human major histocompatibility complex.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Oct;71(4):759-76. doi: 10.1086/342973. Epub 2002 Sep 23. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12297984 Free PMC article.
-
GT repeats are associated with recombination on human chromosome 22.Genome Res. 2000 Aug;10(8):1108-14. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.8.1108. Genome Res. 2000. PMID: 10958629 Free PMC article.
-
iRSpot-TNCPseAAC: identify recombination spots with trinucleotide composition and pseudo amino acid components.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jan 24;15(2):1746-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms15021746. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24469313 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of a novel human acidic nuclease/intra-cyclobutyl-pyrimidine-dimer-DNA phosphodiesterase.Biochem J. 2000 Feb 1;345 Pt 3(Pt 3):583-93. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10642517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990;61:419–36. - PubMed
-
- Andersson L, Lunden A, Sigurdardottir S, Davies CJ, Rask L. Linkage relationships in the bovine MHC region. High recombination frequency between class II subregions. Immunogenetics. 1988;27:273–80. - PubMed
-
- Armour JA, Harris PC, Jeffreys AJ. Allelic diversity at minisatellite MS205 (D16S309): evidence for polarized variability. Human Mol Genet. 1993a;2:1137–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

