Silencer elements controlling the B29 (Igbeta) promoter are neither promoter- nor cell-type-specific
- PMID: 9356446
- PMCID: PMC24921
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12314
Silencer elements controlling the B29 (Igbeta) promoter are neither promoter- nor cell-type-specific
Abstract
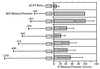
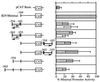
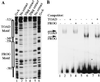
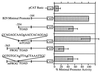
The murine B29 (Igbeta) promoter is B cell specific and contains essential SP1, ETS, OCT, and Ikaros motifs. Flanking 5' DNA sequences inhibit B29 promoter activity, suggesting this region contains silencer elements. Two adjacent 5' DNA segments repress transcription by the murine B29 promoter in a position- and orientation-independent manner, analogous to known silencers. Both these 5' segments also inhibit transcription by several heterologous promoters in B cells, including mb-1, c-fos, and human B29. These 5' segments also inhibit transcription by the c-fos promoter in T cells suggesting they are not B cell-specific elements. DNase I footprint analyses show an approximately 70-bp protected region overlapping the boundary between the two negative regulatory DNA segments and corresponding to binding sites for at least two different DNA-binding proteins. Within this footprint, two unrelated 30-bp cis-acting DNA motifs (designated TOAD and FROG) function as position- and orientation-independent silencers when located directly 5' of the murine B29 promoter. These two silencer motifs act cooperatively to restrict the transcriptional activity of the B29 promoter. Neither of these motifs resembles any known silencers. Mutagenesis of the TOAD and FROG motifs in their respective 5' DNA segments eliminates the silencing activity of these upstream regions, indicating these two motifs as the principal B29 silencer elements within these regions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An upstream Oct-1- and Oct-2-binding silencer governs B29 (Ig beta) gene expression.J Immunol. 2000 Mar 1;164(5):2550-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2550. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10679093
-
The promoter and 5' flanking sequences controlling human B29 gene expression.Blood. 1996 Jan 15;87(2):666-73. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8555489
-
Bob1 (OCA-B/OBF-1) differential transactivation of the B cell-specific B29 (Ig beta) and mb-1 (Ig alpha) promoters.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 1;168(7):3369-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3369. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11907094
-
Transcriptional control and the role of silencers in transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes.Biochem J. 1998 Apr 1;331 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):1-14. doi: 10.1042/bj3310001. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9512455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of non-coding silencer elements and their regulation of gene expression.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;24(6):383-395. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00549-9. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36344659 Review.
Cited by
-
The B29 (immunoglobulin beta-chain) gene is a genetic target for early B-cell factor.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;19(1):392-401. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.1.392. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9858563 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Igβ is essential for the B cell selection in germinal center.Sci Rep. 2015 May 18;5:10303. doi: 10.1038/srep10303. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25980548 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated TCL1 promotes multiple classes of mature B cell lymphoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14392-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212410199. Epub 2002 Oct 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12381789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

