Prominin, a novel microvilli-specific polytopic membrane protein of the apical surface of epithelial cells, is targeted to plasmalemmal protrusions of non-epithelial cells
- PMID: 9356465
- PMCID: PMC24979
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12425
Prominin, a novel microvilli-specific polytopic membrane protein of the apical surface of epithelial cells, is targeted to plasmalemmal protrusions of non-epithelial cells
Abstract
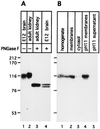
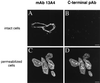
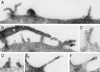
Using a new mAb raised against the mouse neuroepithelium, we have identified and cDNA-cloned prominin, an 858-amino acid-containing, 115-kDa glycoprotein. Prominin is a novel plasma membrane protein with an N-terminal extracellular domain, five transmembrane segments flanking two short cytoplasmic loops and two large glycosylated extracellular domains, and a cytoplasmic C-terminal domain. DNA sequences from Caenorhabditis elegans predict the existence of a protein with the same features, suggesting that prominin is conserved between vertebrates and invertebrates. Prominin is found not only in the neuroepithelium but also in various other epithelia of the mouse embryo. In the adult mouse, prominin has been detected in the brain ependymal layer, and in kidney tubules. In these epithelia, prominin is specific to the apical surface, where it is selectively associated with microvilli and microvilli-related structures. Remarkably, upon expression in CHO cells, prominin is preferentially localized to plasma membrane protrusions such as filopodia, lamellipodia, and microspikes. These observations imply that prominin contains information to be targeted to, and/or retained in, plasma membrane protrusions rather than the planar cell surface. Moreover, our results show that the mechanisms underlying targeting of membrane proteins to microvilli of epithelial cells and to plasma membrane protrusions of non-epithelial cells are highly related.
Figures




References
-
- Nelson W J. Science. 1992;258:948–955. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Boulan E, Powell S K. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:395–427. - PubMed
-
- Simons K, Dupree P, Fiedler K, Huber L A, Kobayashi T, Kurzchalia T, Olkkonen V, Pimplikar S, Parton R, Dotti C. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:611–619. - PubMed
-
- Eaton S, Simons K. Cell. 1995;82:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Mays R W, Nelson W J, Marrs J A. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:763–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

