Transgenic rats reveal functional conservation of regulatory controls between the Fugu isotocin and rat oxytocin genes
- PMID: 9356472
- PMCID: PMC25001
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12462
Transgenic rats reveal functional conservation of regulatory controls between the Fugu isotocin and rat oxytocin genes
Abstract
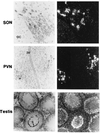
We have asked whether comparative genome analysis and rat transgenesis can be used to identify functional regulatory domains in the gene locus encoding the hypothalamic neuropeptides oxytocin (OT) and vasopressin. Isotocin (IT) and vasotocin (VT) are the teleost homologues of these genes. A contiguous stretch of 46 kb spanning the Fugu IT-VT locus has been sequenced, and nine putative genes were found. Unlike the OT and vasopressin genes, which are closely linked in the mammalian genome in a tail-to-tail orientation, Fugu IT and VT genes are linked head to tail and are separated by five genes. When a cosmid containing the Fugu IT-VT locus was introduced into the rat genome, we found that the Fugu IT gene was specifically expressed in rat hypothalamic oxytocinergic neurons and mimicked the response of the endogenous OT gene to an osmotic stimulus. These data show that cis-acting elements and trans-acting factors mediating the cell-specific and physiological regulation of the OT and IT genes are conserved between mammals and fish. The combination of Fugu genome analysis and transgenesis in a mammal is a powerful tool for identifying and analyzing conserved vertebrate regulatory elements.
Figures




References
-
- Brenner S, Elgar G, Sandford R, Macrae A, Venkatesh B, Aparicio S. Nature (London) 1993;366:265–268. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesh B, Tay B H, Elgar G, Brenner S. J Mol Biol. 1996;259:655–665. - PubMed
-
- How G F, Venkatesh B, Brenner S. Genome Res. 1996;6:1185–1191. - PubMed
-
- Hara Y, Battey J, Gainer H. Mol Brain Res. 1990;8:319–324. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

