Genetic interactions with Rap1 and Ras1 reveal a second function for the fat facets deubiquitinating enzyme in Drosophila eye development
- PMID: 9356481
- PMCID: PMC25022
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12515
Genetic interactions with Rap1 and Ras1 reveal a second function for the fat facets deubiquitinating enzyme in Drosophila eye development
Abstract
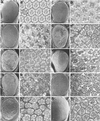
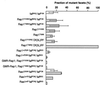
The Drosophila fat facets gene encodes a deubiquitinating enzyme that regulates a cell communication pathway essential very early in eye development, prior to facet assembly, to limit the number of photoreceptor cells in each facet of the compound eye to eight. The Fat facets protein facilitates the production of a signal in cells outside the developing facets that inhibits neural development of particular facet precursor cells. Novel gain-of-function mutations in the Drosophila Rap1 and Ras1 genes are described herein that interact genetically with fat facets mutations. Analysis of these genetic interactions reveals that Fat facets has an additional function later in eye development involving Rap1 and Ras1 proteins. Moreover, the results suggest that undifferentiated cells outside the facet continue to influence facet assembly later in eye development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
All in the family? New insights and questions regarding interconnectivity of Ras, Rap1 and Ral.EMBO J. 1998 Dec 1;17(23):6776-82. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.6776. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9843482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutagenesis screens for interacting genes reveal three roles for fat facets during Drosophila eye development.Dev Genet. 1997;21(2):167-74. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1997)21:2<167::AID-DVG6>3.0.CO;2-5. Dev Genet. 1997. PMID: 9332974
-
The Rap1 GTPase functions as a regulator of morphogenesis in vivo.EMBO J. 1999 Feb 1;18(3):605-15. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.3.605. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9927420 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila roughened mutation: activation of a rap homolog disrupts eye development and interferes with cell determination.Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):717-22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90066-8. Cell. 1991. PMID: 1934069
-
A genetic modifier screen identifies multiple genes that interact with Drosophila Rap/Fzr and suggests novel cellular roles.J Neurogenet. 2007 Jul-Sep;21(3):105-51. doi: 10.1080/01677060701503140. J Neurogenet. 2007. PMID: 17849284 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ras target AF-6 is a substrate of the fam deubiquitinating enzyme.J Cell Biol. 1998 Aug 24;142(4):1053-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.4.1053. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9722616 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila PDZ-GEF, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rap1 GTPase, reveals a novel upstream regulatory mechanism in the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;22(21):7658-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7658-7666.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12370312 Free PMC article.
-
All in the family? New insights and questions regarding interconnectivity of Ras, Rap1 and Ral.EMBO J. 1998 Dec 1;17(23):6776-82. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.6776. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9843482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apical accumulation of the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase during Drosophila eye development is promoted by the small GTPase Rap1.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1237-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.166272. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24899161 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated activation of Rap1 fails to interfere in Ras effector signalling.EMBO J. 1998 Oct 15;17(20):5905-12. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.20.5905. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9774335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeman M. Development (Cambridge, UK) 1997;124:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Zipursky S L, Rubin G M. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:373–397. - PubMed
-
- Heberlein U, Moses K. Cell. 1995;81:987–990. - PubMed
-
- Wolff T, Ready D F. In: The Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Bate M, Matinez Arias A, editors. Vol. 2. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1993. pp. 1277–1326.
-
- Freeman M. Cell. 1996;87:651–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

