Efficient gene tagging in Arabidopsis thaliana using a gene trap approach
- PMID: 9356517
- PMCID: PMC25099
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12722
Efficient gene tagging in Arabidopsis thaliana using a gene trap approach
Abstract
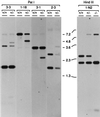
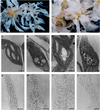
Large quantities of DNA sequence information about plant genes are rapidly accumulating in public databases, but to progress from DNA sequence to biological function a mutant allele for each of the genes ideally should be available. Here we describe a gene trap construct that allowed us to disrupt transcribed genes with a high efficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana. In the T-DNA vector used, the expression of a bacterial reporter gene coding for neomycin phosphotransferase II (nptII) depends on the in vivo generation of a translation fusion upon the T-DNA integration into the Arabidopsis genome. Analysis of 20 selected transgenic lines showed that 12 lines are T-DNA insertion mutants. The disrupted genes analyzed encoded ribosomal proteins (three lines), aspartate tRNA synthase, DNA ligase, basic-domain leucine zipper DNA binding protein, ATP-binding cassette transporter, and five proteins of unknown function. Four tagged genes were new for Arabidopsis. The results presented here suggest that gene trapping, using nptII as a reporter gene, can be as high as 80% and opens novel perspectives for systematic gene tagging in A. thaliana.
Figures
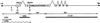
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

