Signal-to-noise measurements in magnitude images from NMR phased arrays
- PMID: 9358462
- PMCID: PMC2570034
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.1910380524
Signal-to-noise measurements in magnitude images from NMR phased arrays
Erratum in
- Magn Reson Med. 2004 Jul;52(1):219
Abstract
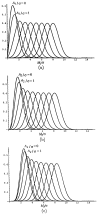
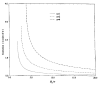
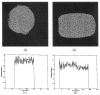
A method is proposed to estimate signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) values in phased array magnitude images, based on a region-of-interest (ROI) analysis. It is shown that the SNR can be found by correcting the measured signal intensity for the noise bias effects and by evaluating the noise variance as the mean square value of all the pixel intensities in a chosen background ROI, divided by twice the number of receivers used. Estimated SNR values are shown to vary spatially within a bound of 20% with respect to the true SNR values as a result of noise correlations between receivers.
Figures

References
-
- Henkelman RM. Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in MR images. Med. Phys. 1984;12:232–233. Erratum in 13, 544 (1986) - PubMed
-
- Henkelman RM, Bronskill MJ. Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging. Rev. of Magn. Reson. Med. 1987;2(1)
-
- Bernstein MA, Thomasson DM, Perman WH. Improved detectability in low signal-to-noise ratio magnetic resonance images by means of a phase-corrected real reconstruction. Med. Phys. 1989;15(5):813–817. - PubMed
-
- Miller AJ, Joseph PM. The use of power images to perform quantitative analysis on low SNR images. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 1993;11:1051–1056. - PubMed
-
- McGibney G, Smith MR. An unbiased signal-to-noise ratio measure for magnetic resonance images. Med. Phys. 1993;20(4):1077–1078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

