Stimulation of NSF ATPase activity by alpha-SNAP is required for SNARE complex disassembly and exocytosis
- PMID: 9362506
- PMCID: PMC2139964
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.4.875
Stimulation of NSF ATPase activity by alpha-SNAP is required for SNARE complex disassembly and exocytosis
Abstract
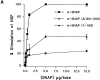
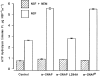
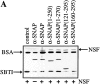
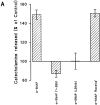
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) and alpha-SNAP play key roles in vesicular traffic through the secretory pathway. In this study, NH2- and COOH-terminal truncation mutants of alpha-SNAP were assayed for ability to bind NSF and stimulate its ATPase activity. Deletion of up to 160 NH2-terminal amino acids had little effect on the ability of alpha-SNAP to stimulate the ATPase activity of NSF. However, deletion of as few as 10 COOH-terminal amino acids resulted in a marked decrease. Both NH2-terminal (1-160) and COOH-terminal (160-295) fragments of alpha-SNAP were able to bind to NSF, suggesting that alpha-SNAP contains distinct NH2- and COOH-terminal binding sites for NSF. Sequence alignment of known SNAPs revealed only leucine 294 to be conserved in the final 10 amino acids of alpha-SNAP. Mutation of leucine 294 to alanine (alpha-SNAP(L294A)) resulted in a decrease in the ability to stimulate NSF ATPase activity but had no effect on the ability of this mutant to bind NSF. alpha-SNAP (1-285) and alpha-SNAP (L294A) were unable to stimulate Ca2+-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized chromaffin cells. In addition, alpha-SNAP (1-285), and alpha-SNAP (L294A) were able to inhibit the stimulation of exocytosis by exogenous alpha-SNAP. alpha-SNAP, alpha-SNAP (1-285), and alpha-SNAP (L294A) were all able to become incorporated into a 20S complex and recruit NSF. In the presence of MgATP, alpha-SNAP (1-285) and alpha-SNAP (L294A) were unable to fully disassemble the 20S complex and did not allow vesicle-associated membrane protein dissociation to any greater level than seen in control incubations. These findings imply that alpha-SNAP stimulation of NSF ATPase activity may be required for 20S complex disassembly and for the alpha-SNAP stimulation of exocytosis.
Figures








References
-
- Beckers CJM, Block MR, Glick BS, Rothman JE, Balch WE. Vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stack requires the NEM-sensitive fusion protein. Nature. 1989;339:397–398. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne, R.D. 1992. Investigation of the intracellular regulators and components of the exocytotic pathway. In Neuromethods, Volume 20: Intracellular Messengers. A. Boulton, G. Baker, and C. Taylor, editors. Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ. 433–470.
-
- Burgoyne RD, Williams G. NSF and SNAP are present on adrenal chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1997;414:349–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

