The O-glycosylated stalk domain is required for apical sorting of neurotrophin receptors in polarized MDCK cells
- PMID: 9362511
- PMCID: PMC2139957
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.4.929
The O-glycosylated stalk domain is required for apical sorting of neurotrophin receptors in polarized MDCK cells
Abstract
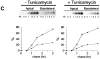
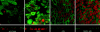
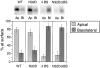
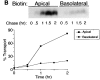
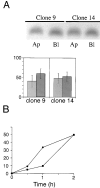
Delivery of newly synthesized membrane-spanning proteins to the apical plasma membrane domain of polarized MDCK epithelial cells is dependent on yet unidentified sorting signals present in the luminal domains of these proteins. In this report we show that structural information for apical sorting of transmembrane neurotrophin receptors (p75(NTR)) is localized to a juxtamembrane region of the extracellular domain that is rich in O-glycosylated serine/threonine residues. An internal deletion of 50 amino acids that removes this stalk domain from p75(NTR) causes the protein to be sorted exclusively of the basolateral plasma membrane. Basolateral sorting stalk-minus p75(NTR) does not occur by default, but requires sequences present in the cytoplasmic domain. The stalk domain is also required for apical secretion of a soluble form of p75(NTR), providing the first demonstration that the same domain can mediate apical sorting of both a membrane-anchored as well as secreted protein. However, the single N-glycan present on p75(NTR) is not required for apical sorting of either transmembrane or secreted forms.
Figures



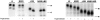


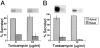


References
-
- Baldwin AN, Shooter EM. Zone mapping of the binding domain of the rat low affinity nerve growth factor receptor by the introduction of novel N-glycosylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4594–4602. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AN, Bitler CM, Welcher AA, Shooter EM. Studies on the structure and binding properties of the cysteine-rich domain of rat low affinity nerve growth factor receptor (p75NGFR) J Biol Chem. 1992;267:8352–8359. - PubMed
-
- Blochberger TC, Sabatine JM, Lee YC, Hughey RP. O-linked glycosylation of rat renal g-glutamylpeptidase adjacent to its membrane anchor domain. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:20718–20722. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Crise B, Rose JK. Mechanism of membrane anchoring affects polarized expression of two proteins in MDCK cells. Science. 1989;245:1499–1501. - PubMed
-
- Casanova JE, Apodaca G, Mostov KE. An autonomous signal for basolateral sorting in the cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Cell. 1991;66:65–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

