Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) interferes with extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation, but does not affect phosphorylation of T cell receptor zeta and ZAP70
- PMID: 9362525
- PMCID: PMC2199134
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.10.1645
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) interferes with extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation, but does not affect phosphorylation of T cell receptor zeta and ZAP70
Abstract
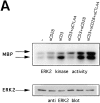
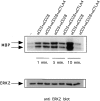
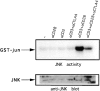
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) is an important regulator of T cell homeostasis. Ligation of this receptor leads to prominent downregulation of T cell proliferation, mainly as a consequence of interference with IL-2 production. We here report that CTLA-4 engagement strikingly selectively shuts off activation of downstream T cell receptor (TCR)/CD28 signaling events, i.e., activation of the microtubule-associated protein kinase (MAPKs) ERK and JNK. In sharp contrast, proximal TCR signaling events such as ZAP70 and TCR-zeta chain phosphorylation are not affected by CTLA-4 engagement on activated T cells. Since activation of the ERK and JNK kinases is required for stimulation of interleukin (IL)-2 transcription, these data provide a molecular explanation for the block in IL-2 production imposed by CTLA-4.
Figures





References
-
- Abbas AK. Die and let live: eliminating dangerous lymphocytes. Cell. 1996;84:655–658. - PubMed
-
- Zheng L, Fisher G, Miller RE, Peschon J, Lynch DH, Lenardo MJ. Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis. Nature (Lond) 1995;377:348–352. - PubMed
-
- Tivol EA, Schweitzer AN, Sharpe AH. Costimulation and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:822–830. - PubMed
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, Linsley PS, Freeman GJ, Green JM, Thompson CB, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

