Signal transduction due to HIV-1 envelope interactions with chemokine receptors CXCR4 or CCR5
- PMID: 9362541
- PMCID: PMC2199136
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.10.1793
Signal transduction due to HIV-1 envelope interactions with chemokine receptors CXCR4 or CCR5
Abstract
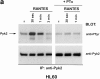
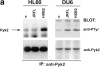
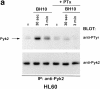
Infection with HIV-1 requires expression of CD4 and the chemokine receptors CXCR4 or CCR5 at the target cell surface. Engagement of these receptors by the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein is essential for membrane fusion, but may additionally activate intracellular signaling pathways. In this study, we demonstrate that chemokines and HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins from both T-tropic and macrophage-tropic strains rapidly induce tyrosine phosphorylation of the protein tyrosine kinase Pyk2. The response requires CXCR4 and CCR5 to be accessible on the cell surface. The results presented here provide the first evidence for activation of an intracellular signaling event that can initiate multiple signaling pathways as a consequence of contact between HIV-1 and chemokine receptors.
Figures





References
-
- Clapham PR, Weiss RA. Spoilt for choice of co-receptors. Nature (Lond) 1997;388:230–231. - PubMed
-
- Wain-Hobson S. HIV. One on one meets two. Nature (Lond) 1996;384:117–118. - PubMed
-
- Hill CM, Littman DR. Natural resistance to HIV? . Nature (Lond) 1996;382:668–669. - PubMed
-
- Fauci AS. Host factors and the pathogenesis of HIV-induced disease. Nature (Lond) 1996;384:529–534. - PubMed
-
- Liu R, Paxton WA, Choe S, Ceradini D, Martin SR, Horuk R, MacDonald ME, Stuhlmann H, Koup RA, Landau NR. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996;86:367–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

