Inhibition of axonal growth by brefeldin A in hippocampal neurons in culture
- PMID: 9364043
- PMCID: PMC6573598
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-08955.1997
Inhibition of axonal growth by brefeldin A in hippocampal neurons in culture
Abstract
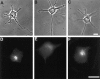
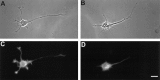
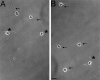
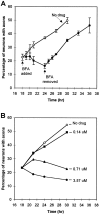
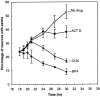
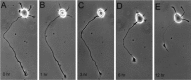
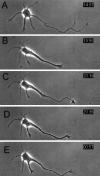
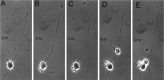
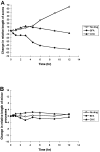
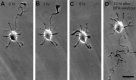
The outgrowth of neuronal processes involves a great increase in the surface area of the cell. The supply of membrane material necessarily must be coordinated with the demands for neurite growth. The selective growth of only one or two neurites at any given time during the development of polarity raises the possibility that the production of materials by the soma is limiting for growth (Dotti and Banker, 1987; Dotti et al., Goslin and Banker, 1990). To examine the role of the availability of membrane components during the development of polarity and axonal elongation, we treated neurons with brefeldin A, an antibiotic that disrupts the trafficking of vesicles from the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. Treatment with brefeldin A (1 microg/ml) inhibited axonal growth within 0.5 hr; in unpolarized cells it prevented the formation of an axon. These results indicate that the availability of membrane components of Golgi-derived vesicles is required for axonal growth and hence the development of polarity. Inhibitors of protein and RNA synthesis also blocked axonal growth and the development of polarity, but over a much slower time course. This suggests that the full complement of proteins and mRNAs required for the initial development of polarity is present for several hours before polarity is actually established.
Figures
References
-
- Akasaki K, Fukuzawa M, Kinoshita H, Furuno K, Tsuji H. Cycling of two endogenous lysosomal membrane proteins, lamp-2 and acid phosphatase, between the cell surface and lysosomes in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1993;114:598–604. - PubMed
-
- Boldin S, Futerman AH. Glucosylceramide synthesis is required for basic fibroblast growth factor and laminin to stimulate axonal growth. J Neurochem. 1997;68:882–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
