Neuronal and non-neuronal collapsin-1 binding sites in developing chick are distinct from other semaphorin binding sites
- PMID: 9364065
- PMCID: PMC6573609
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-09183.1997
Neuronal and non-neuronal collapsin-1 binding sites in developing chick are distinct from other semaphorin binding sites
Abstract
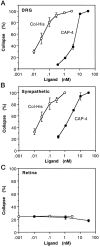
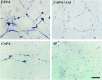
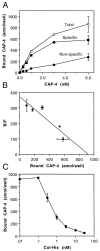
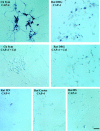
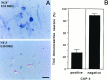
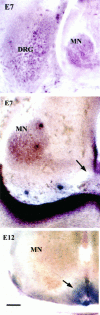
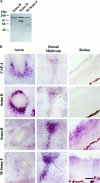
The collapsin and semaphorin family of extracellular proteins contributes to axonal path finding by repulsing axons and collapsing growth cones. To explore the mechanism of collapsin-1 action, we expressed and purified a truncated collapsin-1-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein (CAP-4). This protein retains biological activity as a DRG growth cone collapsing agent and saturably binds to DRG neurons with low nanomolar affinity. Specific CAP-4 binding sites are present on DRG neurons, sympathetic neurons, and motoneurons, but not on retinal, cortical, or brainstem neurons. Outside the nervous system, high levels of CAP-4 binding sites are present in the mesenchyme surrounding major blood vessels and developing bone and in lung. These sites provide a substrate for the collapsin-1-dependent patterning of non-neuronal tissues perturbed in sema III (-/-) mice. The staining patterns for mouse semaphorin D/III and chick collapsin-1 fusion proteins are indistinguishable from one another but quite separate from that for semaphorin B and M-semaphorin F fusion proteins. These data imply that a family of high-affinity semaphorin binding sites similar in complexity to the semaphorin ligand family exists.
Figures
References
-
- Behar O, Golden JA, Mashimo H, Schoen FJ, Fishman MC. Semaphorin III is needed for normal patterning and growth of nerves, bones and heart. Nature. 1996;383:525–528. - PubMed
-
- Camu W, Henderson CE. Purification of embryonic rat motoneuron by panning on a monoclonal antibody to the low-affinity NGF receptor. J Neurosci Methods. 1992;44:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Chen H-J, Flanagan JG. Identification and cloning of ELF-1, a developmentally expressed ligand for the Mek-4 and Sek receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1994;79:157–168. - PubMed
-
- Chen H-J, Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD, Flanagan JG. Complementary gradients in expression and binding of ELF-1 and Mek4 in development of the topographic retinotectal projection map. Cell. 1995;82:371–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
