Differential effects of abnormal tactile experience on shaping representation patterns in developing and adult motor cortex
- PMID: 9364069
- PMCID: PMC6573625
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-09220.1997
Differential effects of abnormal tactile experience on shaping representation patterns in developing and adult motor cortex
Abstract
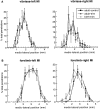
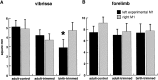
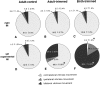
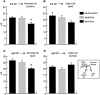
This study investigates the influence of early somatosensory experience on shaping movement representation patterns in motor cortex. Electrical microstimulation was used to map bilaterally the motor cortices of adult rats subjected to altered tactile experience by unilateral vibrissa trimming from birth (birth-trimmed group) or for comparable periods that began in adulthood (adult-trimmed group). Findings demonstrated that (1) vibrissa trimming from birth, but not when initiated in adulthood, led to a significantly smaller-sized primary motor cortex (M1) vibrissa representation in the hemisphere contralateral to the trimmed vibrissae, with no evidence for concomitant changes in size of the adjacent forelimb representation or the representation of the intact vibrissae in the opposite (ipsilateral) hemisphere; (2) in the contralateral hemispheres of the birth-trimmed group, an abnormal pattern of evoked vibrissa movement was evident in which bilateral or ipsilateral (intact) vibrissa movement predominated; (3) in both hemispheres of the birth-trimmed group, current thresholds for eliciting movement of the trimmed vibrissa were significantly lower than normal; and (4) in the adult-trimmed group, but not in the birth-trimmed group, there was a decrease bilaterally in the relative frequency of dual forelimb-vibrissa sites that form the common border between these representations. These results show that sensory experience early in life exerts a significant influence in sculpting motor representation patterns in M1. The mature motor cortex is more resistant to the type and magnitude of influence that tactile experience has on developing M1, which may indicate that such an influence is constrained by a developmentally regulated critical period.
Figures


References
-
- Akhtar ND, Land PW. Activity-dependent regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase in the rat barrel cortex: effects of neonatal versus adult sensory deprivation. J Comp Neurol. 1991;307:200–213. - PubMed
-
- Antonini A, Stryker MP. Rapid remodeling of axonal arbors in the visual cortex. Science. 1993;260:1819–1821. - PubMed
-
- Asanuma H, Arnold AP. Noxious effects of excessive currents used for intracortical microstimulation. Brain Res. 1975;96:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Asanuma H, Arnold AP, Zarzecki P. Further study on the excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1976;26:443–462. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AJ, Gundersen HJG, Cruz-Orive LM. Estimation of surface area from vertical sections. J Microsc. 1986;142:259–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
