Selective synaptic distribution of kainate receptor subunits in the two plexiform layers of the rat retina
- PMID: 9364075
- PMCID: PMC6573580
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-09298.1997
Selective synaptic distribution of kainate receptor subunits in the two plexiform layers of the rat retina
Abstract
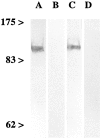
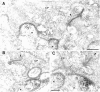
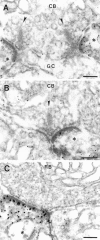
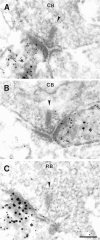
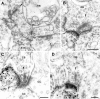
The synaptic localization of the kainate receptor subunits GluR6/7 and KA2 and of the ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits delta1/2 was studied in the rat retina using receptor-specific antisera. GluR6/7 and KA2 were present in both synaptic layers of the retina: the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and the outer plexiform layer (OPL). The localization of delta1/2 was restricted to the IPL. Detailed ultrastructural examination showed that in the OPL GluR6/7 was localized in horizontal cell processes postsynaptic to both rod spherules and cone pedicles. It was always only one of the two invaginating horizontal cell processes at the photoreceptor synapses labeled for GluR6/7. KA2 in the OPL was found only postsynaptic to cone pedicles and never postsynaptic to rod spherules. The KA2-labeled processes made flat contacts with the cone pedicles, suggesting they are the dendrites of OFF bipolar cells. In the IPL the different receptor subunits were localized postsynaptically to ribbon synapses of both rod and cone bipolar cells. As a rule, only one of the two postsynaptic elements at the bipolar cell dyad was stained for each of the receptor subunits examined. The selective and heterogeneous distribution of these receptors at the ribbon synapses of the OPL and IPL suggests a high degree of differential processing of the glutamatergic signals.
Figures


References
-
- Araki K, Meguro H, Kushiya E, Takayama C, Inoue Y, Mishina M. Selective expression of the glutamate receptor channel delta 2 subunit in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;197:1267–1276. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Egebjerg J, Sharma G, Pecht G, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Moll C, Stevens CF, Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992;8:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Boycott BB. Horizontal cells of mammalian retinae. Neurosci Res [Suppl] 1988;8:97–111. - PubMed
-
- Brandstätter JH, Hartveit E, Sassoè-Pognetto M, Wässle H. Expression of NMDA and high-affinity kainate receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult rat retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1994;6:1100–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
