The Arabidopsis HY5 gene encodes a bZIP protein that regulates stimulus-induced development of root and hypocotyl
- PMID: 9367981
- PMCID: PMC316701
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.22.2983
The Arabidopsis HY5 gene encodes a bZIP protein that regulates stimulus-induced development of root and hypocotyl
Abstract
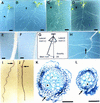
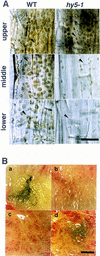
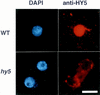
Plant developmental processes are controlled by both endogenous programs and environmental stimuli. As a photomorphogenetic mutant, hy5 of Arabidopsis has been isolated and characterized. Our detailed characterization has revealed that the mutant is deficient in a variety of stimulus responses, including gravitropic response and waving growth of roots, as well as light-dependent hypocotyl elongation. In the roots and hypocotyl, the hy5 mutation also affects greening and specific cell proliferation such as lateral root formation and secondary thickening. Those phenotypes indicate that the HY5 gene is responsible for the regulation of fundamental developmental processes of the plant cell: cell elongation, cell proliferation, and chloroplast development. Molecular cloning of the HY5 gene using a T-DNA-tagged mutant has revealed that the gene encodes a protein with a bZIP motif, one of the motifs found in transcriptional regulators. Nuclear localization of the HY5 protein strongly suggests that the HY5 gene modulates the signal transduction pathways under the HY5-related development by controlling expression of genes downstream of these pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Aeschbacher RA, Schiefelbein JW, Benfey PN. The genetic and molecular basis of root development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1994;45:25–45.
-
- Ahmad M, Cashmore AR. HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor. Nature. 1993;366:162–166. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, NY: Greene/Wiley; 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
