Inhibition of NF-kappaB DNA binding and nitric oxide induction in human T cells and lung adenocarcinoma cells by selenite treatment
- PMID: 9371773
- PMCID: PMC24236
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12904
Inhibition of NF-kappaB DNA binding and nitric oxide induction in human T cells and lung adenocarcinoma cells by selenite treatment
Abstract
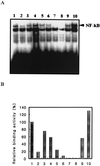
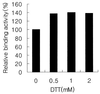
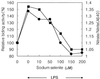
NF-kappaB is a major transcription factor consisting of 50(p50)- and 65(p65)-kDa proteins that controls the expression of various genes, among which are those encoding cytokines, cell adhesion molecules, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS). After initial activation of NF-kappaB, which involves release and proteolysis of a bound inhibitor, essential cysteine residues are maintained in the active reduced state through the action of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. In the present study, activation of NF-kappaB in human T cells and lung adenocarcinoma cells was induced by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha or bacterial lipopolysaccharide. After lipopolysaccharide activation, nuclear extracts were treated with increasing concentrations of selenite, and the effects on DNA-binding activity of NF-kappaB were examined. Binding of NF-kappaB to nuclear responsive elements was decreased progressively by increasing selenite levels and, at 7 microM selenite, DNA-binding activity was completely inhibited. Selenite inhibition was reversed by addition of a dithiol, DTT. Proportional inhibition of iNOS activity as measured by decreased NO products in the medium (NO2- and NO3-) resulted from selenite addition to cell suspensions. This loss of iNOS activity was due to decreased synthesis of NO synthase protein. Selenium at low essential levels (nM) is required for synthesis of redox active selenoenzymes such as glutathione peroxidases and thioredoxin reductase, but in higher toxic levels (>5-10 microM) selenite can react with essential thiol groups on enzymes to form RS-Se-SR adducts with resultant inhibition of enzyme activity. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity by selenite is presumed to be the result of adduct formation with the essential thiols of this transcription factor.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

