The Tabby phenotype is caused by mutation in a mouse homologue of the EDA gene that reveals novel mouse and human exons and encodes a protein (ectodysplasin-A) with collagenous domains
- PMID: 9371801
- PMCID: PMC24264
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.13069
The Tabby phenotype is caused by mutation in a mouse homologue of the EDA gene that reveals novel mouse and human exons and encodes a protein (ectodysplasin-A) with collagenous domains
Abstract
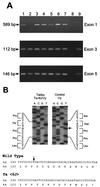
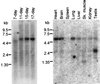
Mouse Tabby (Ta) and X chromosome-linked human EDA share the features of hypoplastic hair, teeth, and eccrine sweat glands. We have cloned the Ta gene and find it to be homologous to the EDA gene. The gene is altered in two Ta alleles with a point mutation or a deletion. The gene is expressed in developing teeth and epidermis; no expression is seen in corresponding tissues from Ta mice. Ta and EDA genes both encode alternatively spliced forms; novel exons now extend the 3' end of the EDA gene. All transcripts recovered have the same 5' exon. The longest Ta cDNA encodes a 391-residue transmembrane protein, ectodysplasin-A, containing 19 Gly-Xaa-Yaa repeats. The isoforms of ectodysplasin-A may correlate with differential roles during embryonic development.
Figures


References
-
- Falconer D S. Nature (London) 1952;169:664–665. - PubMed
-
- Blecher S R. J Invest Dermatol. 1986;87:720–722. - PubMed
-
- Sundberg J P. Handbook of Mouse Mutations with Skin and Hair Abnormalities. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1994. pp. 455–462.
-
- McKusick V A. Mendelian Inheritance in Man. 11th Ed. Baltimore and London: Johns Hopkins Univ. Press; 1994.
-
- Cattanach B M, Rasberry C, Evans E P, Dandolo L, Simmler M C, Avner P. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;56:137–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

