Btk dosage determines sensitivity to B cell antigen receptor cross-linking
- PMID: 9371815
- PMCID: PMC24278
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.13152
Btk dosage determines sensitivity to B cell antigen receptor cross-linking
Abstract
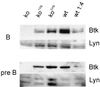
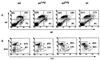
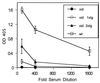
Mutations in Btk result in the B cell immunodeficiencies X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) in humans and X-linked immunodeficiency (xid) in mice. Btk is a critical component of signaling pathways regulating B cell development and function. We used a genetic approach to determine whether Btk is also limiting for these processes. One allele of a murine Btk transgene expressed a dosage of Btk (25% of endogenous levels in splenic B cells) sufficient to restore normal numbers of phenotypically mature conventional B cells in xid mice. 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl-Ficoll response, anti-IgM-induced proliferation, B1 cell development, and serum IgM and IgG3 levels remained significantly impaired in these animals. B cells from Btk -/- transgenic mice also responded poorly to anti-IgM, indicating that the xid mutation does not create a dominant negative form of Btk. Response to 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl-Ficoll and B cell receptor cross-linking were increased 3- to 4-fold in xid mice homozygous for the transgene. These results demonstrate that Btk is a limiting component of B cell antigen receptor signaling pathways and suggest that B cell development and response to antigen may require different levels of Btk activity.
Figures

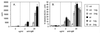
References
-
- Carter R H, Fearon D T. Science. 1992;256:105–107. - PubMed
-
- Engel P, Zhou L-J, Ord D C, Sato S, Koller B, Tedder T F. Immunity. 1995;3:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Lund F E, Yu N, Kim K-M, Reth M, Howard M C. J Immunol. 1996;157:1455–1467. - PubMed
-
- Pezzutto A, Rabinovitch P S, Dorken B, Moldenhauer G, Clark E A. J Immunol. 1988;140:1791–1795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

