Terpenoid biosynthesis from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose in higher plants by intramolecular skeletal rearrangement
- PMID: 9380681
- PMCID: PMC23416
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10600
Terpenoid biosynthesis from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose in higher plants by intramolecular skeletal rearrangement
Abstract
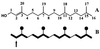
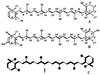
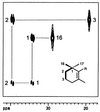
The incorporation of [1-13C]- and [2,3,4,5-13C4]1-deoxy-D-xylulose into beta-carotene, lutein, phytol, and sitosterol in a cell culture of Catharanthus roseus was analyzed by NMR spectroscopy. The labeling patterns of the isoprene precursors, isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, were obtained from the terpenes by a retrobiosynthetic approach. 13C Enrichment and 13C13C coupling patterns showed conclusively that 1-deoxy-D-xylulose and not mevalonate is the predominant isoprenoid precursor of phytol, beta-carotene, and lutein. Label from 1-deoxyxylulose was also diverted to phytosterols to a minor extent (6% relative to carotene and phytol formation). The data demonstrate that the formation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate from pentulose occurs strictly by an intramolecular rearrangement process.
Figures



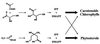
References
-
- Popják G, Cornforth J W. Adv Enzymol. 1960;22:281–335. - PubMed
-
- Bloch K. Steroids. 1992;57:378–383. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin T W. In: Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Pigments. Goodwin T W, editor. London: Academic; 1965. pp. 143–154.
-
- Loomis W D. In: Terpenoids in Plants. Pridham J B, editor. London: Academic; 1967. pp. 59–82.
-
- Banthorpe D V, Charlwood B V, Francis M J O. Chem Rev. 1972;72:115–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

