Hypo-phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) by cyclin D:Cdk4/6 complexes results in active pRb
- PMID: 9380698
- PMCID: PMC23451
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10699
Hypo-phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) by cyclin D:Cdk4/6 complexes results in active pRb
Abstract
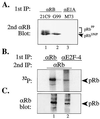
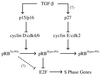
In cycling cells, the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) is un- and/or hypo-phosphorylated in early G1 and becomes hyper-phosphorylated in late G1. The role of hypo-phosphorylation and identity of the relevant kinase(s) remains unknown. We show here that hypo-phosphorylated pRb associates with E2F in vivo and is therefore active. Increasing the intracellular concentration of the Cdk4/6 specific inhibitor p15(INK4b) by transforming growth factor beta treatment of keratinocytes results in G1 arrest and loss of hypo-phosphorylated pRb with an increase in unphosphorylated pRb. Conversely, p15(INK4b)-independent transforming growth factor beta-mediated G1 arrest of hepatocellular carcinoma cells results in loss of Cdk2 kinase activity with continued Cdk6 kinase activity and pRb remains only hypo-phosphorylated. Introduction of the Cdk4/6 inhibitor p16(INK4a) protein into cells by fusion to a protein transduction domain also prevents pRb hypo-phosphorylation with an increase in unphosphorylated pRb. We conclude that cyclin D:Cdk4/6 complexes hypo-phosphorylate pRb in early G1 allowing continued E2F binding.
Figures
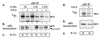



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

