Immunologic tolerance to myelin basic protein decreases stroke size after transient focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 9380727
- PMCID: PMC23514
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10873
Immunologic tolerance to myelin basic protein decreases stroke size after transient focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
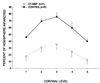
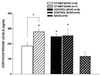
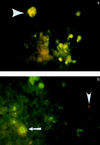
Immune mechanisms contribute to cerebral ischemic injury. Therapeutic immunosuppressive options are limited due to systemic side effects. We attempted to achieve immunosuppression in the brain through oral tolerance to myelin basic protein (MBP). Lewis rats were fed low-dose bovine MBP or ovalbumin (1 mg, five times) before 3 h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). A third group of animals was sensitized to MBP but did not survive the post-stroke period. Infarct size at 24 and 96 h after ischemia was significantly less in tolerized animals. Tolerance to MBP was confirmed in vivo by a decrease in delayed-type hypersensitivity to MBP. Systemic immune responses, characterized in vitro by spleen cell proliferation to Con A, lipopolysaccharide, and MBP, again confirmed antigen-specific immunologic tolerance. Immunohistochemistry revealed transforming growth factor beta1 production by T cells in the brains of tolerized but not control animals. Systemic transforming growth factor beta1 levels were equivalent in both groups. Corticosterone levels 24 h after surgery were elevated in all sham-operated animals and ischemic control animals but not in ischemic tolerized animals. These results demonstrate that antigen-specific modulation of the immune response decreases infarct size after focal cerebral ischemia and that sensitization to the same antigen may actually worsen outcome.
Figures



References
-
- Kondo Y, Ogawa N, Asanuma M, Nishibayashi S, Iwata E, Mori A. Neurosci Res. 1995;22:123–127. - PubMed
-
- Wakita H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Kimura J. Stroke. 1995;26:1415–1422. - PubMed
-
- Sharkey J, Butcher S P. Nature (London) 1994;371:336–339. - PubMed
-
- Tokime T, Nozaki K, Kikuchi H. Neurosci Lett. 1996;206:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Khoury S J, Lider O, Al-Sabbagh A, Weiner H L. Cell Immunol. 1990;131:301–310. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

