Supervillin (p205): A novel membrane-associated, F-actin-binding protein in the villin/gelsolin superfamily
- PMID: 9382871
- PMCID: PMC2140202
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.5.1255
Supervillin (p205): A novel membrane-associated, F-actin-binding protein in the villin/gelsolin superfamily
Abstract
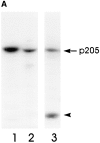
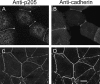
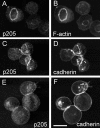
Actin-binding membrane proteins are involved in both adhesive interactions and motile processes. We report here the purification and initial characterization of p205, a 205-kD protein from bovine neutrophil plasma membranes that binds to the sides of actin filaments in blot overlays. p205 is a tightly bound peripheral membrane protein that cosediments with endogenous actin in sucrose gradients and immunoprecipitates. Amino acid sequences were obtained from SDS-PAGE-purified p205 and used to generate antipeptide antibodies, immunolocalization data, and cDNA sequence information. The intracellular localization of p205 in MDBK cells is a function of cell density and adherence state. In subconfluent cells, p205 is found in punctate spots along the plasma membrane and in the cytoplasm and nucleus; in adherent cells, p205 concentrates with E-cadherin at sites of lateral cell-cell contact. Upon EGTA-mediated cell dissociation, p205 is internalized with E-cadherin and F-actin as a component of adherens junctions "rings." At later times, p205 is observed in cytoplasmic punctae. The high abundance of p205 in neutrophils and suspension-grown HeLa cells, which lack adherens junctions, further suggests that this protein may play multiple roles during cell growth, adhesion, and motility. Molecular cloning of p205 cDNA reveals a bipartite structure. The COOH terminus exhibits a striking similarity to villin and gelsolin, particularly in regions known to bind F-actin. The NH2 terminus is novel, but contains four potential nuclear targeting signals. Because p205 is now the largest known member of the villin/gelsolin superfamily, we propose the name, "supervillin." We suggest that supervillin may be involved in actin filament assembly at adherens junctions and that it may play additional roles in other cellular compartments.
Figures















References
-
- Aberle H, Schwartz H, Kemler R. Cadherin-catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function. J Cell Biochem. 1996;61:514–523. - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Amer J Physiol. 1995;269:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson PH. HeLa cell plasma membranes. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:157–188. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1989. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

