Effects of sleep on wake-induced c-fos expression
- PMID: 9391027
- PMCID: PMC6573405
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-24-09746.1997
Effects of sleep on wake-induced c-fos expression
Abstract
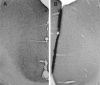
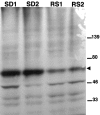
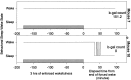
We investigated the effects of sleep on wake-induced c-fos expression in the cerebral cortex of rats and c-fos-lacZ transgenic mice. In the cortex of rats, the levels of c-Fos, detected both by immunocytochemistry and Western blot, remained high during 6 or 12 hr of enforced wakefulness but declined rapidly (within 1 hr) with increasing time of recovery sleep. Similarly, in the transgenic mice in which lacZ expression is driven from the c-fos promoter, beta-galactosidase activity was high after enforced wakefulness and declined with increasing amounts of sleep. These results suggest that the decrease in c-Fos protein in cortical neurons during sleep may be attributable to cessation of c-fos expression, activation of a process that degrades the wake-induced c-Fos, or both.
Figures



References
-
- Cirelli C, Tononi G. Changes in protein phosphorylation patterns in the brain during the sleep-waking cycle. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1996;22:688.
-
- Cirelli C, Pompeiano M, Tononi G. Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain in spontaneous wakefulness and sleep. Arch Ital Biol. 1993a;131:327–330. - PubMed
-
- Cirelli C, Pompeiano M, Tononi G. Fos expression in the rat brain after variable periods of sleep deprivation. Sleep Res. 1993b;22:595. - PubMed
-
- Cirelli C, Pompeiano M, Tononi G. Sleep deprivation and c-fos expression in the rat brain. J Sleep Res. 1995;4:92–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
