Multiple pathways for SOS-induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli: an overexpression of dinB/dinP results in strongly enhancing mutagenesis in the absence of any exogenous treatment to damage DNA
- PMID: 9391106
- PMCID: PMC28386
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13792
Multiple pathways for SOS-induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli: an overexpression of dinB/dinP results in strongly enhancing mutagenesis in the absence of any exogenous treatment to damage DNA
Abstract
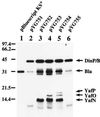
dinP is an Escherichia coli gene recently identified at 5.5 min of the genetic map, whose product shows a similarity in amino acid sequence to the E. coli UmuC protein involved in DNA damage-induced mutagenesis. In this paper we show that the gene is identical to dinB, an SOS gene previously localized near the lac locus at 8 min, the function of which was shown to be required for mutagenesis of nonirradiated lambda phage infecting UV-preirradiated bacterial cells (termed lambdaUTM for lambda untargeted mutagenesis). A newly constructed dinP null mutant exhibited the same defect for lambdaUTM as observed previously with a dinB::Mu mutant, and the defect was complemented by plasmids carrying dinP as the only intact bacterial gene. Furthermore, merely increasing the dinP gene expression, without UV irradiation or any other DNA-damaging treatment, resulted in a strong enhancement of mutagenesis in F'lac plasmids; at most, 800-fold increase in the G6-to-G5 change. The enhanced mutagenesis did not depend on recA, uvrA, or umuDC. Thus, our results establish that E. coli has at least two distinct pathways for SOS-induced mutagenesis: one dependent on umuDC and the other on dinB/P.
Figures

References
-
- Friedberg E C, Walker G C, Siede W. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol. Press; 1995.
-
- Echols H, Goodman M F. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:477–511. - PubMed
-
- Witkin E M, Wermundsen I E. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1978;43:881–886. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Shinoura Y. Mol Gen Genet. 1977;156:121–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

