Interferon-gamma impacts at multiple points during the progression of autoimmune diabetes
- PMID: 9391115
- PMCID: PMC28395
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13844
Interferon-gamma impacts at multiple points during the progression of autoimmune diabetes
Abstract
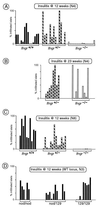
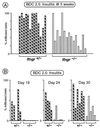
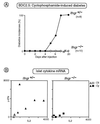
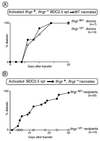
The role of interferon-gamma in autoimmune diabetes was assessed by breeding a null mutation of the interferon-gamma receptor alpha chain into the nonobese diabetic mouse strain, as well as into a simplified T cell receptor transgenic model of diabetes. In contrast to a previous report on abrogation of the interferon-gamma gene, mutation of the gene encoding its receptor led to drastic effects on disease in both mouse lines. Nonobese diabetic mice showed a marked inhibition of insulitis-both the kinetics and penetrance-and no signs of diabetes; the transgenic model exhibited near-normal insulitis, but this never evolved into diabetes, either spontaneously or after experimental provocation. This failure could not be explained by perturbations in the ratio of T helper cell phenotypes; rather, it reflected a defect in antigen-presenting cells or in the islet beta cell targets.
Figures
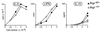
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

