The virtual visit: using telecommunications technology to take care of patients
- PMID: 9391929
- PMCID: PMC61259
- DOI: 10.1136/jamia.1997.0040413
The virtual visit: using telecommunications technology to take care of patients
Abstract
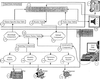
Telephone-Linked Care (TLC) technology has been developed and applied as an alternative to and a supplement for office visits as a means to deliver ambulatory care. TLC is used to monitor patients with chronic diseases, counsel patients on important health behaviors, and provide information and support to home caregivers of patients with disabling conditions. TLC speaks to patients over the telephone in their homes using computer-controlled digitized human speech. Patients use their telephone keypad to communicate. TLC conversations last 2-15 minutes per call and take place weekly for periods of at least 3 months. The conversations consist of a salutation, password verification, the core clinical part, and a closing. The structure of the clinical part is similar for each of the application groups: chronic disease, health behavior, and caregiver support. The system architecture consists of linked voice and database components and their subcomponents. Preliminary evaluation indicates that TLC is well accepted by patients and their providers and can improve clinical outcomes.
Figures



References
-
- Schappert SM. National ambulatory medical care survey: 1991 summary. Vital Health Stat. 1994;116: 1-110. - PubMed
-
- Hallam L. You've got a lot to answer for, Mr. Bell: a review of the use of the telephone in primary care. Fam Pract. 1989;6: 47-57. - PubMed
-
- Scannell KM, Perednia DA, Kissman HM. Telemedicine: past, present, future. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Public Health Service, USDHHS, 1995.
-
- Spencer DC, Daugird AJ: The nature and content of physician telephone calls in a private practice. J Fam Pract. 1988;27: 201-5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

