Export of cellubrevin from the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by BAP31
- PMID: 9396746
- PMCID: PMC2132629
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.6.1397
Export of cellubrevin from the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by BAP31
Abstract
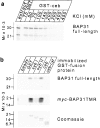
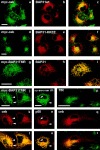
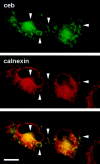
Cellubrevin is a ubiquitously expressed membrane protein that is localized to endosomes throughout the endocytotic pathway and functions in constitutive exocytosis. We report that cellubrevin binds with high specificity to BAP31, a representative of a highly conserved family of integral membrane proteins that has recently been discovered to be binding proteins of membrane immunoglobulins. The interaction between BAP31 and cellubrevin is sensitive to high ionic strength and appears to require the transmembrane regions of both proteins. No other proteins of liver membrane extracts copurified with BAP31 on immobilized recombinant cellubrevin, demonstrating that the interaction is specific. Synaptobrevin I bound to BAP31 with comparable affinity, whereas only weak binding was detectable with synaptobrevin II. Furthermore, a fraction of BAP31 and cellubrevin was complexed when each of them was quantitatively immunoprecipitated from detergent extracts of fibroblasts (BHK 21 cells). During purification of clathrin-coated vesicles or early endosomes, BAP31 did not cofractionate with cellubrevin. Rather, the protein was enriched in ER-containing fractions. When BHK cells were analyzed by immunocytochemistry, BAP31 did not overlap with cellubrevin, but rather colocalized with resident proteins of the ER. In addition, immunoreactive vesicles were clustered in a paranuclear region close to the microtubule organizing center, but different from the Golgi apparatus. When microtubules were depolymerized with nocodazole, this accumulation disappeared and BAP31 was confined to the ER. Truncation of the cytoplasmic tail of BAP31 prevented export of cellubrevin, but not of the transferrin receptor from the ER. We conclude that BAP31 represents a novel class of sorting proteins that controls anterograde transport of certain membrane proteins from the ER to the Golgi complex.
Figures







References
-
- Aridor M, Balch WE. Principles of selective transport: coat complexes hold the key. Trends Cell Biol. 1996;6:315–320. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, McCaffery JM, Plutner H, Farquhar MG. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is sorted and concentrated during export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;76:841–852. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Armherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

