Ligation of major histocompatability complex (MHC) class I molecules on human T cells induces cell death through PI-3 kinase-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activity: a novel apoptotic pathway distinct from Fas-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 9396757
- PMCID: PMC2132618
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.6.1523
Ligation of major histocompatability complex (MHC) class I molecules on human T cells induces cell death through PI-3 kinase-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activity: a novel apoptotic pathway distinct from Fas-induced apoptosis
Abstract
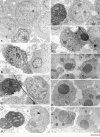
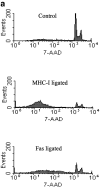
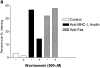
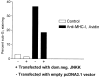
Ligation of major histocompatability complex class I (MHC-I) molecules expressed on T cells leads to both growth arrest and apoptosis. The aim of the current study was to investigate the intracellular signal pathways that mediate these effects. MHC-I ligation of human Jurkat T cells induced a morphologically distinct form of apoptosis within 6 h. A specific caspase inhibitor, which inhibited Fas-induced apoptosis, did not affect apoptosis induced by MHC-I ligation. Furthermore, MHC-I-induced apoptosis did not involve cleavage and activation of the poly(ADP- ribose) polymerase (PARP) endonuclease or degradation of genomic DNA into the typical fragmentation ladder, both prominent events of Fas-induced apoptosis. These results suggest that MHC-I ligation of Jurkat T cells induce apoptosis through a signal pathway distinct from the Fas molecule. In our search for other signal pathways leading to apoptosis, we found that the regulatory 85-kD subunit of the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI-3) kinase was tyrosine phosphorylated after ligation of MHC-I and the PI-3 kinase inhibitor wortmannin selectively blocked MHC-I-, but not Fas-induced, apoptosis. As the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) can be activated by PI-3 kinase activity, and has been shown to be involved in apoptosis of lymphocytes, we examined JNK activation after MHC-I ligation. Strong JNK activity was observed after MHC-I ligation and the activity was completely blocked by wortmannin. Inhibition of JNK activity, by transfecting cells with a dominant-negative JNKK- MKK4 construct, led to a strong reduction of apoptosis after MHC-I ligation. These results suggest a critical engagement of PI-3 kinase-induced JNK activity in apoptosis induced by MHC-I ligation.
Figures









References
-
- Apasov S, Redegeld F, Sitkovsky M. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity: contact and secreted factors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993;5:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Beckwith M, Fenton RG, Katona IM, Longo DL. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity is required for the anti–ig-mediated growth inhibition of a human B-lymphoma cell line. Blood. 1996;87:202–210. - PubMed
-
- Bregenholt S, Röpke M, Skov S, Claesson MH. Ligation of MHC class I molecules on peripheral blood T lymphocytes induces new phenotypes and functions. JImmunol. 1996;157:993–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

