RGS2/G0S8 is a selective inhibitor of Gqalpha function
- PMID: 9405622
- PMCID: PMC24991
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.26.14389
RGS2/G0S8 is a selective inhibitor of Gqalpha function
Abstract
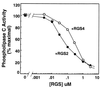
RGS (regulators of G protein signaling) proteins are GTPase activating proteins that inhibit signaling by heterotrimeric G proteins. All RGS proteins studied to date act on members of the Gialpha family, but not Gsalpha or G12alpha. RGS4 regulates Gialpha family members and Gqalpha. RGS2 (G0S8) is exceptional because the G proteins it regulates have not been identified. We report that RGS2 is a selective and potent inhibitor of Gqalpha function. RGS2 selectively binds Gqalpha, but not other Galpha proteins (Gi, Go, Gs, G12/13) in brain membranes; RGS4 binds Gqalpha and Gialpha family members. RGS2 binds purified recombinant Gqalpha, but not Goalpha, whereas RGS4 binds either. RGS2 does not stimulate the GTPase activities of Gsalpha or Gialpha family members, even at a protein concentration 3000-fold higher than is sufficient to observe effects of RGS4 on Gialpha family members. In contrast, RGS2 and RGS4 completely inhibit Gq-directed activation of phospholipase C in cell membranes. When reconstituted with phospholipid vesicles, RGS2 is 10-fold more potent than RGS4 in blocking Gqalpha-directed activation of phospholipase Cbeta1. These results identify a clear physiological role for RGS2, and describe the first example of an RGS protein that is a selective inhibitor of Gqalpha function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The GTPase-activating protein RGS4 stabilizes the transition state for nucleotide hydrolysis.J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 1;271(44):27209-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27209. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8910288
-
Regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) and RGS4 form distinct G protein-dependent complexes with protease activated-receptor 1 (PAR1) in live cells.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 17;9(4):e95355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095355. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24743392 Free PMC article.
-
Novel activity of RGS14 on Goalpha and Gialpha nucleotide binding and hydrolysis distinct from its RGS domain and GDI activity.Biochemistry. 2005 Apr 12;44(14):5495-502. doi: 10.1021/bi048359d. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15807543
-
RGS2: a multifunctional regulator of G-protein signaling.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002 May;34(5):432-8. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00141-8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11906816 Review.
-
Application of RGS box proteins to evaluate G-protein selectivity in receptor-promoted signaling.Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:71-88. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89005-0. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 15313560 Review.
Cited by
-
RGS2 modulates the activity and internalization of dopamine D2 receptors in neuroblastoma N2A cells.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Nov;110(Pt A):297-307. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27528587 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of alpha2-adrenergic receptor-mediated Gi signalling by a novel pathway.Biochem J. 1999 Oct 1;343 Pt 1(Pt 1):77-85. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10493914 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension and prolonged vasoconstrictor signaling in RGS2-deficient mice.J Clin Invest. 2003 Feb;111(4):445-52. doi: 10.1172/JCI15598. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12588882 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of RGS2 suggests a novel mechanism in G-protein signaling and neuronal plasticity.J Neurosci. 1998 Sep 15;18(18):7178-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-18-07178.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9736641 Free PMC article.
-
Thinking outside of the "RGS box": new approaches to therapeutic targeting of regulators of G protein signaling.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;78(4):550-7. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.065219. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20664002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

