Neurokinin 1 receptor expression in the rat retina
- PMID: 9414009
- PMCID: PMC3696024
Neurokinin 1 receptor expression in the rat retina
Abstract
Tachykinin (TK) peptides influence neuronal activity in the inner retina of mammals. The aim of this investigation was to determine the cellular localization of the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1), whose preferred ligand is the TK peptide substance P (SP), in the rat retina. These studies used a polyclonal antiserum directed to the C-terminus of rat NK1. The majority of NK1-immunoreactive (IR) cells were located in the proximal inner nuclear layer (INL), and very rarely they were found in the distal INL. Some small and large NK1-IR somata were present in the ganglion cell layer. NK1-IR processes were densely distributed across the inner plexiform layer (IPL) with a maximum density over lamina 2 of the IPL. Immunoreactive processes also crossed the INL and ramified in the outer plexiform layer where they formed a sparse meshwork. NK1-IR processes were rarely observed in the optic nerve fiber layer. Double-label immunofluorescence studies with different histochemical markers for bipolar cells indicated that NK1 immunoreactivity was not present in bipolar cells. Together, these observations indicate that NK1 immunoreactivity is predominantly expressed by amacrine, displaced amacrine, interplexiform, and some ganglion cells. Double-label immunofluorescence experiments were also performed to characterize NK1-containing amacrine cells. Sixty-one percent of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-IR cells, 71% of the large tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-IR cells, and 100% of the small TH-IR cells contained NK1 immunoreactivity. In addition, most (91%) of the NK1-IR cells had GABA immunoreactivity. In contrast, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, TK-, choline acetyltransferase-, and parvalbumin-IR amacrine tells did not express NK1 immunoreactivity. Overall, the present findings suggest that SP acts directly upon several cell populations, including GABA-containing amacrine cells and ganglion cells, to influence visual information processing in the inner retina.
Figures
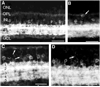
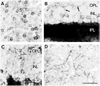
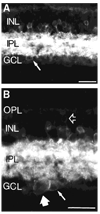
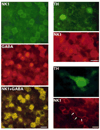
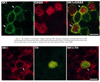

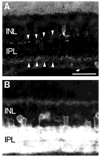
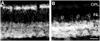
Similar articles
-
Postnatal development of NK1, NK2, and NK3 neurokinin receptors expression in the rat retina.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999 Oct 20;117(1):59-70. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(99)00099-1. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10536233
-
Developmental expression of neurokinin-1 and neurokinin-3 receptors in the rat retina.J Comp Neurol. 2000 May 29;421(2):275-87. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10813787
-
Localization of GABA, glycine, glutamate and tyrosine hydroxylase in the human retina.J Comp Neurol. 1992 Jan 15;315(3):287-302. doi: 10.1002/cne.903150305. J Comp Neurol. 1992. PMID: 1346792
-
Expression of the neurokinin 1 receptor in the rabbit retina.Neuroscience. 2002;115(4):1309-21. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00408-6. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12453499
-
Morphologic maturation of tachykinin peptide-expressing cells in the postnatal rabbit retina.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997 Apr 18;99(2):131-41. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(96)00206-4. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9125466
Cited by
-
Retinal laser burn-induced neuropathy leads to substance P-dependent loss of ocular immune privilege.J Immunol. 2012 Aug 1;189(3):1237-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103264. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22745377 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and synaptic organization of substance P-like immunoreactive neurons in the mouse retina.Brain Struct Funct. 2023 Sep;228(7):1703-1724. doi: 10.1007/s00429-023-02688-x. Epub 2023 Jul 23. Brain Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 37481742
-
Localization of neuropeptide Y1 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat retina and the synaptic connectivity of Y1 immunoreactive cells.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Dec 23;454(4):373-82. doi: 10.1002/cne.10423. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12455004 Free PMC article.
-
Tachykinin-related peptide and GABA-mediated presynaptic inhibition of crayfish photoreceptors.J Neurosci. 2000 Mar 1;20(5):1780-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-05-01780.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10684879 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-inhibition of NMBR and GRPR signaling maintains normal histaminergic itch transmission.J Neurosci. 2014 Sep 10;34(37):12402-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1709-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25209280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brecha NC, Hendrickson A, Floren I, Karten HJ. Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity within the monkey retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1982;23:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Brecha NC, Eldred W, Kuljis RO, Karten HJ. Identification and localization of biologically active peptides in the vertebrate retina. In: Osborne NN, Chader GJ, editors. Progress in Retinal Research. Vol. 3. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1984. pp. 185–226.
-
- Brecha NC, Sternini C, Anderson K, Krause JE. Expression and cellular localization of substance P/neurokinin A and neurokinin B mRNAs in the rat retina. Visual Neurosci. 1989;3:527–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

