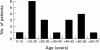Clinical characteristics of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults
- PMID: 9414977
- PMCID: PMC1891582
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.41.5.675
Clinical characteristics of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults
Abstract
Background: Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, a syndrome of ineffectual motility due to a primary disorder of enteric nerve or muscle, is rare.
Aims: To determine the clinical spectrum, underlying pathologies, response to treatments, and prognosis in a consecutive unselected group of patients.
Methods: Cross sectional study of all patients with clinical and radiological features of intestinal obstruction in the absence of organic obstruction, associated with dilated small intestine (with or without dilated large intestine), being actively managed in one tertiary referral centre at one time.
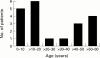
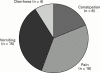
Results: Twenty patients (11 men and nine women, median age 43 years, range 22-67) fulfilled the diagnostic criteria. Median age at onset of symptoms was 17 years (range two weeks to 59 years). Two patients had an autosomally dominant inherited visceral myopathy. Major presenting symptoms were pain (80%), vomiting (75%), constipation (40%), and diarrhoea (20%). Eighteen patients required abdominal surgery, and a further patient had a full thickness rectal biopsy. The mean time interval from symptom onset to first operation was 5.8 years. Histology showed visceral myopathy in 13, visceral neuropathy in three, and was indeterminate in three. In the one other patient small bowel motility studies were suggestive of neuropathy. Two patients died within two years of symptom onset, one from generalised thrombosis and the other from an inflammatory myopathy. Of the remaining 18 patients, eight were nutritionally independent of supplements, two had gastrostomy or jejunostomy feeds, and eight were receiving home parenteral nutrition. Five patients were opiate dependent, only one patient had benefited from prokinetic drug therapy, and five patients required formal psychological intervention and support.
Conclusions: In a referral setting visceral myopathy is the most common diagnosis in this heterogeneous syndrome, the course of the illness is usually prolonged, and prokinetic drug therapies are not usually helpful. Ongoing management problems include pain relief and nutritional support.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural history of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults: a single center study.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 May;3(5):449-58. doi: 10.1016/s1542-3565(04)00675-5. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 15880314
-
Four cases with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction due to hollow visceral myopathy.Hepatogastroenterology. 1999 Jan-Feb;46(25):349-52. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. PMID: 10228819
-
[Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction].Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006 Aug-Sep;30(8-9):975-85. doi: 10.1016/s0399-8320(06)73359-0. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006. PMID: 17075444 Review. French.
-
[Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: visceral myopathy. Report of 4 cases].Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam. 1993;23(4):239-43. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam. 1993. PMID: 8203187 Review. Spanish.
-
[Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus].Rev Med Interne. 2011 Jan;32(1):e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2010.03.458. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Rev Med Interne. 2011. PMID: 21035926 French.
Cited by
-
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction.Gut. 2000 Dec;47 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):iv84; discussion iv87. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.suppl_4.iv84. Gut. 2000. PMID: 11076928 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Horses for courses. Comparative gastroenterology: common ground and collaborative potential.BMJ. 2005 Nov 26;331(7527):1248-51. doi: 10.1136/bmj.331.7527.1248. BMJ. 2005. PMID: 16308386 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
[Motility disorders of the small intestine].Internist (Berl). 2015 Jun;56(6):631-7. doi: 10.1007/s00108-014-3606-7. Internist (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25854121 Review. German.
-
Emergency surgery in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction due to mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy: case reports.Int Arch Med. 2010 Dec 8;3:35. doi: 10.1186/1755-7682-3-35. Int Arch Med. 2010. PMID: 21143863 Free PMC article.
-
Natural History of Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction and Need for Palliative Care.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023 Jul 30;29(3):378-387. doi: 10.5056/jnm22152. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023. PMID: 37417265 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical