Tau91, an essential subunit of yeast transcription factor IIIC, cooperates with tau138 in DNA binding
- PMID: 9418847
- PMCID: PMC121441
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.1.1
Tau91, an essential subunit of yeast transcription factor IIIC, cooperates with tau138 in DNA binding
Abstract
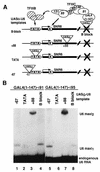
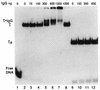
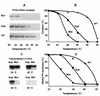
Transcription factor IIIC (TFIIIC) (or tau) is a large multisubunit and multifunctional factor required for transcription of all class III genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is responsible for promoter recognition and TFIIIB assembly. We report here the cloning and characterization of TFC6, an essential gene encoding the 91-kDa polypeptide, tau91, present in affinity-purified TFIIIC. Tau91 has a predicted molecular mass of 74 kDa. It harbors a central cluster of His and Cys residues and has basic and acidic amino acid regions, but it shows no specific similarity to known proteins or predicted open reading frames. The TFIIIC subunit status of tau91 was established by the following biochemical and genetic evidence. Antibodies to tau91 bound TFIIIC-DNA complexes in gel shift assays; in vivo, a B block-deficient U6 RNA gene (SNR6) harboring GAL4 binding sites was reactivated by fusing the GAL4 DNA binding domain to tau91; and a point mutation in TFC6 (tau91-E330K) was found to suppress the thermosensitive phenotype of a tfc3-G349E mutant affected in the B block binding subunit (tau138). The suppressor mutation alleviated the DNA binding and transcription defects of mutant TFIIIC in vitro. These results indicated that tau91 cooperates with tau138 for DNA binding. Recombinant tau91 by itself did not interact with a tRNA gene, although it showed a strong affinity for single-stranded DNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic interactions within TFIIIC, the promoter-binding factor of yeast RNA polymerase III.Mol Genet Genomics. 2001 Jun;265(4):705-10. doi: 10.1007/s004380100467. Mol Genet Genomics. 2001. PMID: 11459191
-
Identical components of yeast transcription factor IIIB are required and sufficient for transcription of TATA box-containing and TATA-less genes.Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2798-808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2798-2808.1994. Mol Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8139577 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in the largest subunit of yeast TFIIIC affects tRNA and 5 S RNA synthesis. Identification of two classes of suppressors.J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):23374-81. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8083243
-
The tau95 subunit of yeast TFIIIC influences upstream and downstream functions of TFIIIC.DNA complexes.J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 21;278(12):10450-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M213310200. Epub 2003 Jan 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12533520
-
Comparison of the RNA polymerase III transcription machinery in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2675-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2675. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A chimeric subunit of yeast transcription factor IIIC forms a subcomplex with tau95.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;18(6):3191-200. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.6.3191. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9584160 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and kinetic insights into tRNA promoter engagement by yeast general transcription factor TFIIIC.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 7;53(1):gkae1174. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39657784 Free PMC article.
-
A novel subunit of yeast RNA polymerase III interacts with the TFIIB-related domain of TFIIIB70.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(2):488-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.2.488-495.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10611227 Free PMC article.
-
The TFIIIC90 subunit of TFIIIC interacts with multiple components of the RNA polymerase III machinery and contains a histone-specific acetyltransferase activity.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7697-704. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7697. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523658 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of two evolutionarily conserved subunits (TFIIIC102 and TFIIIC63) of human TFIIIC and their involvement in functional interactions with TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Jul;19(7):4944-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4944. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10373544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartholomew B, Meares C F, Dahmus M E. Photoaffinity labelling of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by nascent RNA. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:3731–3737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
