Nuclear accumulation of p21Cip1 at the onset of mitosis: a role at the G2/M-phase transition
- PMID: 9418901
- PMCID: PMC121522
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.1.546
Nuclear accumulation of p21Cip1 at the onset of mitosis: a role at the G2/M-phase transition
Abstract
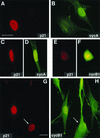
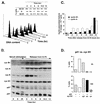
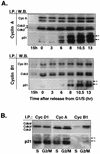
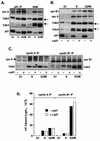
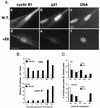
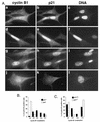
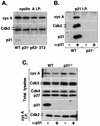
Cell cycle arrest in G1 in response to ionizing radiation or senescence is believed to be provoked by inactivation of G1 cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) by the Cdk inhibitor p21(Cip1/Waf1/Sdi1). We provide evidence that in addition to exerting negative control of the G1/S phase transition, p21 may play a role at the onset of mitosis. In nontransformed fibroblasts, p21 transiently reaccumulates in the nucleus near the G2/M-phase boundary, concomitant with cyclin B1 nuclear translocation, and associates with a fraction of cyclin A-Cdk and cyclin B1-Cdk complexes. Premitotic nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 is not detectable in cells with low p21 levels, such as fibroblasts expressing the viral human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein, which functionally inactivates p53, or in tumor-derived cells. Moreover, synchronized E6-expressing fibroblasts show accelerated entry into mitosis compared to wild-type cells and exhibit higher cyclin A- and cyclin B1-associated kinase activities. Finally, primary embryonic fibroblasts derived from p21-/- mice have significantly reduced numbers of premitotic cells with nuclear cyclin B1. These data suggest that p21 promotes a transient pause late in G2 that may contribute to the implementation of late cell cycle checkpoint controls.
Figures
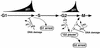
Similar articles
-
Delta MEKK3:ER* activation induces a p38 alpha/beta 2-dependent cell cycle arrest at the G2 checkpoint.Oncogene. 2002 Nov 21;21(53):8089-104. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206000. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12444545
-
Transient suppression of nuclear Cdc2 activity in response to ionizing radiation.Oncol Rep. 2008 May;19(5):1323-9. Oncol Rep. 2008. PMID: 18425394
-
Deregulation of p53/p21Cip1/Waf1 pathway contributes to polyploidy and apoptosis of E1A+cHa-ras transformed cells after gamma-irradiation.Oncogene. 1999 Oct 7;18(41):5611-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202945. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10523840
-
Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 5;20(15):1803-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204252. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313928 Review.
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
Cited by
-
4-Hydroxynonenal induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest by activation of the ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related protein (ATR)/checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20532-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467662. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23733185 Free PMC article.
-
High concentrations of HGF inhibit skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation in vitro by inducing expression of myostatin: a possible mechanism for reestablishing satellite cell quiescence in vivo.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):C465-76. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00449.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20007454 Free PMC article.
-
G2/M checkpoint regulation and apoptosis facilitate the nuclear egress of parvoviral capsids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 8;10:1070599. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1070599. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36568985 Free PMC article.
-
p53-dependent G2 arrest associated with a decrease in cyclins A2 and B1 levels in a human carcinoma cell line.Br J Cancer. 2000 Feb;82(3):642-50. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.0976. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10682678 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of p21(waf1) in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells and its association with cyclin A/cdk2.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(16):7270-83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.16.7270-7283.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10906181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aprelikova O, Xiong Y, Liu E T. Both p16 and p21 families of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors block the phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases by the CDK-activating kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18195–18197. - PubMed
-
- Bailly E, Pines J, Hunter T, Bornens M. Cytoplasmic accumulation of cyclin B1 in human cells: association with a detergent-resistant compartment and with the centrosome. J Cell Sci. 1992;101:529–545. - PubMed
-
- Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote M J, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7:812–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
