Role of UEV-1, an inactive variant of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, in in vitro differentiation and cell cycle behavior of HT-29-M6 intestinal mucosecretory cells
- PMID: 9418904
- PMCID: PMC121525
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.1.576
Role of UEV-1, an inactive variant of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, in in vitro differentiation and cell cycle behavior of HT-29-M6 intestinal mucosecretory cells
Abstract
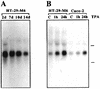
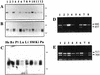
By means of differential RNA display, we have isolated a cDNA corresponding to transcripts that are down-regulated upon differentiation of the goblet cell-like HT-29-M6 human colon carcinoma cell line. These transcripts encode proteins originally identified as CROC-1 on the basis of their capacity to activate transcription of c-fos. We show that these proteins are similar in sequence, and in predicted secondary and tertiary structure, to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2. Despite the similarities, these proteins lack a critical cysteine residue essential for the catalytic activity of E2 enzymes and, in vitro, they do not conjugate or transfer ubiquitin to protein substrates. These proteins constitute a distinct subfamily within the E2 protein family and are highly conserved in phylogeny from yeasts to mammals. Therefore, we have designated them UEV (ubiquitin-conjugating E2 enzyme variant) proteins, defined as proteins similar in sequence and structure to the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes but lacking their enzymatic activity (HW/GDB-approved gene symbol, UBE2V). At least two human genes code for UEV proteins, and one of them, located on chromosome 20q13.2, is expressed as at least four isoforms, generated by alternative splicing. All human cell types analyzed expressed at least one of these isoforms. Constitutive expression of exogenous human UEV in HT-29-M6 cells inhibited their capacity to differentiate upon confluence and caused both the entry of a larger proportion of cells in the division cycle and an accumulation in G2-M. This was accompanied with a profound inhibition of the mitotic kinase, cdk1. These results suggest that UEV proteins are involved in the control of differentiation and could exert their effects by altering cell cycle distribution.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Fusion of the human gene for the polyubiquitination coeffector UEV1 with Kua, a newly identified gene.Genome Res. 2000 Nov;10(11):1743-56. doi: 10.1101/gr.gr-1405r. Genome Res. 2000. PMID: 11076860 Free PMC article.
-
A homologue of CROC-1 in a ciliated protist (Sterkiella histriomuscorum) testifies to the ancient origin of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variant family.Mol Biol Evol. 2002 Jan;19(1):39-48. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003980. Mol Biol Evol. 2002. PMID: 11752188
-
Identification and characterization of UEV3, a human cDNA with similarities to inactive E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Dec 12;1579(2-3):219-24. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00543-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12427560
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C: a potential cancer biomarker.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;47:113-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361302 Review.
-
Diverse roles of the E2/E3 hybrid enzyme UBE2O in the regulation of protein ubiquitination, cellular functions, and disease onset.FEBS J. 2019 Jun;286(11):2018-2034. doi: 10.1111/febs.14708. Epub 2018 Dec 4. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 30468556 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomewide RNA expression profiling in lung identifies distinct signatures in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and secondary pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Apr;298(4):H1235-48. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00254.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20081107 Free PMC article.
-
Uev1A promotes breast cancer cell survival and chemoresistance through the AKT-FOXO1-BIM pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Dec 9;19:331. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1050-4. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31827405 Free PMC article.
-
Linc00426 accelerates lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating miR-455-5p as a molecular sponge.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Dec 11;11(12):1051. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03259-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33311443 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity, origin, and evolution of the ESCRT systems.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0033524. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00335-24. Epub 2024 Feb 21. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38380930 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion of the human gene for the polyubiquitination coeffector UEV1 with Kua, a newly identified gene.Genome Res. 2000 Nov;10(11):1743-56. doi: 10.1101/gr.gr-1405r. Genome Res. 2000. PMID: 11076860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arion D, Meijer L, Brizuela L, Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988;55:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Bailly V, Lamb J, Sung P, Prakash S, Prakash L. Specific complex formation between yeast RAD6 and RAD18 proteins: a potential mechanism for targeting RAD6 ubiquitin-conjugating activity to DNA damage sites. Genes Dev. 1994;8:811–820. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A, Deshaies R J, Chau V. Characterization of a dominant negative mutant of the cell cycle ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:26209–26215. - PubMed
-
- Barila D, Murgia C, Nobili F, Gaetani S, Perozzi G. Subtractive hybridization cloning of novel genes differentially expressed during intestinal development. Eur J Biochem. 1994;223:701–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
