Human IAP-like protein regulates programmed cell death downstream of Bcl-xL and cytochrome c
- PMID: 9418907
- PMCID: PMC121528
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.1.608
Human IAP-like protein regulates programmed cell death downstream of Bcl-xL and cytochrome c
Abstract
The gene encoding human IAP-like protein (hILP) is one of several mammalian genes with sequence homology to the baculovirus inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein (iap) genes. Here we show that hILP can block apoptosis induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli, including UV light, chemotoxic drugs, and activation of the tumor necrosis factor and Fas receptors. hILP also protected against cell death induced by members of the caspase family, cysteine proteases which are thought to be the principal effectors of apoptosis. hILP and Bcl-xL were compared for their ability to affect several steps in the apoptotic pathway. Redistribution of cytochrome c from mitochondria, an early event in apoptosis, was not blocked by overexpression of hILP but was inhibited by Bcl-xL. In contrast, hILP, but not Bcl-xL, inhibited apoptosis induced by microinjection of cytochrome c. These data suggest that while Bcl-xL may control mitochondrial integrity, hILP can function downstream of mitochondrial events to inhibit apoptosis.
Figures
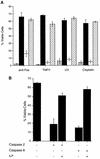
 ), pEBB-hILP (▪), pCI (□), or pCI-Bcl-xL (▨). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with fresh medium or medium supplemented with either anti-Fas antibody and cycloheximide, rhTNF-α, or cisplatin or were exposed to UV. After 12 h, cells were fixed, stained for β-galactosidase expression, and scored for apoptotic morphology. (B) MCF7F cells were transfected with pCMV-lacZ together with pcDNA3, pcDNA3-caspase 2, or pcDNA3-caspase 8 with or without cotransfection of pEBB-hILP expression vector. At 24 h after transfection, cells were fixed, stained for β-galactosidase expression, and scored for apoptotic morphology. Results are expressed as percent viable cells (number of flat blue cells/number of flat and round blue cells × 100). The data represent means ± standard deviations (n = 3).
), pEBB-hILP (▪), pCI (□), or pCI-Bcl-xL (▨). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with fresh medium or medium supplemented with either anti-Fas antibody and cycloheximide, rhTNF-α, or cisplatin or were exposed to UV. After 12 h, cells were fixed, stained for β-galactosidase expression, and scored for apoptotic morphology. (B) MCF7F cells were transfected with pCMV-lacZ together with pcDNA3, pcDNA3-caspase 2, or pcDNA3-caspase 8 with or without cotransfection of pEBB-hILP expression vector. At 24 h after transfection, cells were fixed, stained for β-galactosidase expression, and scored for apoptotic morphology. Results are expressed as percent viable cells (number of flat blue cells/number of flat and round blue cells × 100). The data represent means ± standard deviations (n = 3).
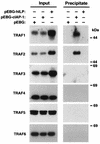
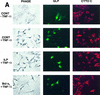



References
-
- Alnemri E S, Livingston D J, Nicholson D W, Salvesen G, Thornberry N A, Wong W W, Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996;87:171. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong R, Aja T, Xiang J, Gaur S, Krebs J, Hoang K, Bai X, Korsmeyer S, Karanewsky D, Fritz L, Tomaselli K. Fas-induced activation of the cell death related protease CPP32 is inhibited by Bcl-2 and by ICE family protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16850–16855. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, R. C. Unpublished observations.
-
- Bertin J, Armstrong R C, Ottilie S, Martin D A, Wang Y, Banks S, Wang G H, Senkevich T G, Alnemri E S, Moss B, Lenardo M J, Tomaselli K J, Cohen J I. Death effector domain-containing herpesvirus and poxvirus proteins inhibit both Fas- and TNFR1-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:1172–1176. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
