Shortage of mitogen-activated protein kinase is responsible for resistance to AP-1 transactivation and transformation in mouse JB6 cells
- PMID: 9419345
- PMCID: PMC18158
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.156
Shortage of mitogen-activated protein kinase is responsible for resistance to AP-1 transactivation and transformation in mouse JB6 cells
Abstract
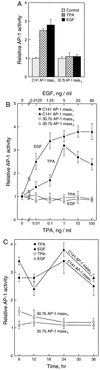
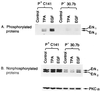
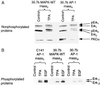
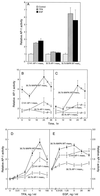
The JB6 mouse epidermal cell system, which includes tumor promotion-sensitive (P+) and tumor promotion-resistant (P-) cells, is a well-established and extensively used cell culture model for studying the mechanism of late-stage tumor promotion. Tumor promoters, such as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) or epidermal growth factor (EGF), induce high levels of activator protein 1 (AP-1) activity and large, tumorigenic, anchorage-independent colonies in soft agar at a high frequency in JB6 P+ cells, but not in JB6 P- cells. We report here a molecular explanation for the defect in the AP-1 activation and promotion-resistant phenotype of P- cells. We demonstrate that the lack of AP-1 activation and cell transformation responses to TPA and EGF in P- cells appears attributable to the low level of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase, Erk) in these cells. TPA and EGF induce transactivation of AP-1 activity in P+ cells but not in P- cells. Nonphosphorylated forms and TPA- or EGF-induced phosphorylated forms of Erks (Erk1 and Erk2) in P- cells were much lower than those in P+ cells. Stable transfection of wild-type MAPK (Erk2) into P- cells restored its response to TPA and EGF for both AP-1 activation and cell transformation. These results suggest that the shortage of MAPK (Erk1 and Erk2) appears to be an important contributor to the tumor promotion-resistant phenotype in JB6 cells.
Figures
References
-
- Boutwell R K. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1964;4:207–250. - PubMed
-
- Drinkwater N R. In: Genes and Signal Transduction in Multistage Carcinogenesis. Colburn N, editor. New York: Dekker; 1989. pp. 3–17.
-
- Dong Z, Jeffrey A M. Cancer Invest. 1990;8:523–533. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein I B. Cancer Res. 1988;48:4135–4143. - PubMed
-
- Colburn N H, Former B F, Nelson K A, Yuspa S H. Nature (London) 1979;281:589–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

