Controlling signaling with a specifically designed Gi-coupled receptor
- PMID: 9419379
- PMCID: PMC18222
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.352
Controlling signaling with a specifically designed Gi-coupled receptor
Abstract
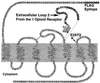
We are developing a system to control G protein signaling in vivo to regulate a broad range of physiologic responses. Our system utilizes G protein-coupled peptide receptors engineered to respond exclusively to synthetic small molecule ligands and not to their natural ligand(s). These engineered receptors are designated RASSLs (receptor activated solely by a synthetic ligand). We have made two prototype RASSLs that are based on the human kappa opioid receptor. Small molecule drugs that activate the kappa receptor are nonaddictive and safe to administer in vivo. Binding and signaling assays reveal 200-2000-fold reductions in the ability of our RASSLs to bind or be activated by dynorphin, an endogenous peptide ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. In a high-throughput signaling assay, these prototype RASSLs expressed in Chinese hamster ovary K1 cells showed little or no response to a panel of 21 opioid peptides but still signaled normally in response to small molecule drugs such as spiradoline. Activation of a RASSL by spiradoline also caused proliferation of rat-1a tissue culture cells. These data provide evidence that G protein-coupled receptors can be made into RASSLs. The potential in vivo applications for RASSLs include the positive enrichment of transfected cells and the development of new animal models of disease.
Figures




References
-
- Strader C D, Fong T M, Tota M R, Underwood D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:101–132. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel A M, Shenker A, Weinstein L S. Endocr Rev. 1992;13:536–565. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin J M. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:180–190. - PubMed
-
- Conklin B R, Bourne H R. Cell. 1993;73:631–641. - PubMed
-
- Bourne H R. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:134–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

