Transcription factor Sp1 mediates cell-specific trans-activation of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene promoter by immediate-early protein IE86 in glioblastoma U373MG cells
- PMID: 9420220
- PMCID: PMC109369
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.1.236-244.1998
Transcription factor Sp1 mediates cell-specific trans-activation of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene promoter by immediate-early protein IE86 in glioblastoma U373MG cells
Abstract
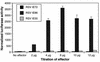
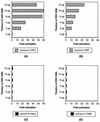
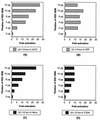
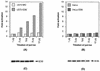
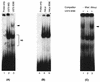
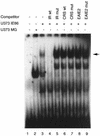
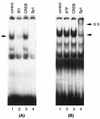
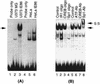
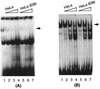
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gene expression is highly cell and tissue specific. Cell factor-mediated regulatory interactions are involved in regulating the restricted expression of the HCMV major immediate-early (IE) gene (J. F. Baskar, P. P. Smith, G. Nilaver, R. A. Jupp, S. Hoffmann, N. J. Peffer, D. J. Tenney, A. M. Colberg-Poley, P. Ghazal, and J. A. Nelson, 70:3207-3213, 1996). To gain an understanding of HCMV early gene activation, we studied the effect of each of the three major IE proteins, IE72, IE86, and IE55, on the HCMV DNA polymerase gene (pol; UL54) promoter. In transient-expression assays, the IE86 protein alone was able to transactivate the pol promoter, but IE72 and IE55 were not, in permissive U373MG cells. However, we were unable to detect IE86-mediated transactivation in nonpermissive HeLa or C33-A cells. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs), we found that expression of the IE86 protein in U373MG cells resulted in specific binding of a DNA complex to an inverted-repeat element, IR1, of the pol promoter. Antibody supershifting and EMSA-Western blotting experiments further showed that IE86 and the cellular transcription factor Sp1 were components of the IR1 DNA-binding complex. Furthermore, we found that binding of DNA by Sp1 was dramatically increased in the presence of IE86. Interestingly, this IE86-induced DNA-binding activity of Sp1 was inhibited by a repressor activity presented in HeLa cells. In summary, our study suggests that a viral regulatory protein can modulate the DNA binding activity of a cellular transcription factor, resulting in cell-specific transactivation of viral genes.
Figures

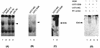
Similar articles
-
Binding of SP1 to the immediate-early protein-responsive element of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase promoter.J Virol. 1997 Sep;71(9):6683-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.9.6683-6691.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9261391 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction between the human cytomegalovirus 86-kilodalton IE2 protein and the cellular transcription factor CREB.J Virol. 1995 Oct;69(10):6030-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.10.6030-6037.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7666507 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein can block cell cycle progression after inducing transition into the S phase of permissive cells.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(15):7108-18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.7108-7118.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10888651 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and regulation of human cytomegalovirus early genes.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):361-77. doi: 10.1159/000150507. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130046 Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus and human herpesvirus 6 genes that transform and transactivate.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999 Jul;12(3):367-82. doi: 10.1128/CMR.12.3.367. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10398670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The intracellular DNA sensor IFI16 gene acts as restriction factor for human cytomegalovirus replication.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002498. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002498. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22291595 Free PMC article.
-
Dominance of virus over host factors in cross-species activation of human cytomegalovirus early gene expression.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(1):26-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.1.26-35.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11119570 Free PMC article.
-
Development of cell lines that provide tightly controlled temporal translation of the human cytomegalovirus IE2 proteins for complementation and functional analyses of growth-impaired and nonviable IE2 mutant viruses.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(14):7059-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00675-08. Epub 2008 May 7. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18463148 Free PMC article.
-
The 6-aminoquinolone WC5 inhibits human cytomegalovirus replication at an early stage by interfering with the transactivating activity of viral immediate-early 2 protein.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 May;54(5):1930-40. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01730-09. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20194695 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US4-1 inhibits CD8(+) T cell responses by targeting the aminopeptidase ERAP1.Nat Immunol. 2011 Sep 4;12(10):984-91. doi: 10.1038/ni.2097. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21892175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baskar J F, Smith P P, Nilaver G, Jupp R A, Hoffmann S, Peffer N J, Tenney D J, Colberg-Poley A M, Ghazal P, Nelson J A. The enhancer domain of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter determines cell type-specific expression in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1996;70:3207–3214. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G, Dorsch-Hasler K, Fleckenstein B, Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985;41:521–530. - PubMed
-
- Briggs M R, Kadonaga J T, Bell S P, Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor. Science. 1986;234:47–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

