Characterization of cis-acting and NS1 protein-responsive elements in the p6 promoter of parvovirus B19
- PMID: 9420265
- PMCID: PMC109414
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.1.609-616.1998
Characterization of cis-acting and NS1 protein-responsive elements in the p6 promoter of parvovirus B19
Abstract
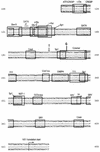
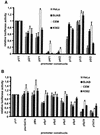
Parvovirus B19 infections are associated with diverse clinical manifestations, ranging from no symptoms to severe symptoms. The virus shows an extreme tropism for replication in erythroid progenitor cells, possibly due to the activity of the only functional promoter (p6) of the B19 virus genome in combination with both cell- and cell cycle-specific factors and the trans-activator protein NS1. As presented here, p6 promoter sequences derived from several B19 virus isolates proved to be highly conserved. Furthermore, mutations did not affect any of the potential binding sites for transcription factors. One variation of the base at position 223 was identified only in B19 virus isolates derived from patients with persistent infection or chronic arthritis. To determine promoter activity and to characterize regulatory elements, sequences spanning the total p6 promoter and subfragments of them were introduced into a eukaryotic expression vector upstream of the luciferase gene (from Photinus pyralis). After transfection into HeLa, CEM, BJAB, and K562 cells, the p6 promoter was found to be highly active. When introduced into the erythroid cell line K562, p6-controlled transcription exceeded that of the simian virus 40 promoter-enhancer used as a control by more than 25-fold. Sequence elements relevant for promoter activity mapped to the regions from nucleotides (nt) 100 to 190 and 233 to 298. Also, the segment from nt 343 to 400 downstream of the TATA box was important for transcriptional activity in HeLa and K562 cells. By transfecting the promoter-luciferase constructs into a HeLa cell line stably carrying the viral NS1 gene under the control of an inducible promoter, transcriptional activity mediated by the p6 promoter rose significantly after induction of NS1 expression. The region from nt 100 to 160 proved to be essential for NS1-mediated transcriptional activation. Furthermore, NS1-mediated transactivation was dependent on the presence of two GC-rich elements arranged in tandem upstream of the TATA box. These data indicate that NS1-mediated p6 transactivation is dependent on a multicomponent complex combining NS1 with ATF, NF-kappaB/c-Rel, and GC-box binding cellular factors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The effects of the 11 kDa protein and the putative X protein on the p6 promoter activity of Parvovirus B19 in Hela cells.Virus Genes. 2013 Feb;46(1):167-9. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0839-1. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Virus Genes. 2013. PMID: 23114653
-
NS1 protein of parvovirus B19 interacts directly with DNA sequences of the p6 promoter and with the cellular transcription factors Sp1/Sp3.Virology. 2002 Feb 1;293(1):86-93. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1285. Virology. 2002. PMID: 11853402
-
DNA Binding and Cleavage by the Human Parvovirus B19 NS1 Nuclease Domain.Biochemistry. 2016 Nov 29;55(47):6577-6593. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00534. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27809499 Free PMC article.
-
Unscrambling the role of human parvovirus B19 signaling in systemic autoimmunity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1453-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.04.023. Epub 2006 May 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16764828 Review.
-
New Insights of Human Parvovirus B19 in Modulating Erythroid Progenitor Cell Differentiation.Viral Immunol. 2020 Oct;33(8):539-549. doi: 10.1089/vim.2020.0013. Epub 2020 May 15. Viral Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32412895 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter by human parvovirus B19 NS1 through activation of AP-1 and AP-2.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(11):5395-403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5395-5403.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11991968 Free PMC article.
-
A Functional Minigenome of Parvovirus B19.Viruses. 2022 Jan 4;14(1):84. doi: 10.3390/v14010084. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35062288 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the 11 kDa protein and the putative X protein on the p6 promoter activity of Parvovirus B19 in Hela cells.Virus Genes. 2013 Feb;46(1):167-9. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0839-1. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Virus Genes. 2013. PMID: 23114653
-
Recent Advances in Replication and Infection of Human Parvovirus B19.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 5;8:166. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00166. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29922597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Parvovirus B19 genotype 2 in KU812Ep6 cells.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):14197-206. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.14197-14206.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson M J, Jones S E, Fisher-Hoch S P, Lewis E, Hall S M, Bartlett C L R, Cohen B J, Mortimer P P, Pereira M S. Human parvovirus, the cause of erythema infectiosum (fifth disease)? Lancet. 1983;i:1378. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel I, editor. Current protocols in molecular biology. 1 to 3. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons; 1995.
-
- Blundell M C, Astell C R. In vitro identification of a B19 parvovirus promoter. Virology. 1987;157:534–538. - PubMed
-
- Brown K E, Anderson S M, Young N S. Erythrocyte P antigen: cellular receptor for the B19 virus. Science. 1993;262:1192–1196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

