A prokaryotic-like mode of cytoplasmic eukaryotic ribosome binding to the initiation codon during internal translation initiation of hepatitis C and classical swine fever virus RNAs
- PMID: 9420332
- PMCID: PMC316404
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.1.67
A prokaryotic-like mode of cytoplasmic eukaryotic ribosome binding to the initiation codon during internal translation initiation of hepatitis C and classical swine fever virus RNAs
Abstract
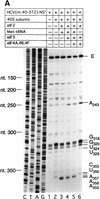
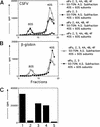
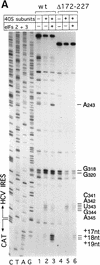
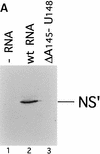
Initiation of translation of hepatitis C virus and classical swine fever virus mRNAs results from internal ribosomal entry. We reconstituted internal ribosomal entry in vitro from purified translation components and monitored assembly of 48S ribosomal preinitiation complexes by toe-printing. Ribosomal subunits (40S) formed stable binary complexes on both mRNAs. The complex structure of these RNAs determined the correct positioning of the initiation codon in the ribosomal "P" site in binary complexes. Ribosomal binding and positioning on these mRNAs did not require the initiation factors eIF3, eIF4A, eIF4B, and eIF4F and translation of these mRNAs was not inhibited by a trans-dominant eIF4A mutant. Addition of Met-tRNAiMet, eIF2, and GTP to these binary ribosomal complexes resulted in formation of 48S preinitiation complexes. The striking similarities between this eukaryotic initiation mechanism and the mechanism of translation initiation in prokaryotes are discussed.
Figures













References
-
- Anthony DD, Merrick WC. Analysis of 40S and 80S complexes with mRNA as measured by sucrose density gradients and primer extension inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1554–1562. - PubMed
-
- Baker A-M, Draper DE. Messenger RNA recognition by fragments of ribosomal protein S4. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22939–22945. - PubMed
-
- Benne R, Hershey JWB. The mechanism of action of protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:3078–3087. - PubMed
-
- Benne R, Brown-Luedi ML, Hershey JWB. Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation factors eIF-1, eIF-4C, eIF-4D, and eIF-5 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:3070–3077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
