Identification and cloning of waaF (rfaF) from Bordetella pertussis and use to generate mutants of Bordetella spp. with deep rough lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 9422589
- PMCID: PMC106845
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.1.35-40.1998
Identification and cloning of waaF (rfaF) from Bordetella pertussis and use to generate mutants of Bordetella spp. with deep rough lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
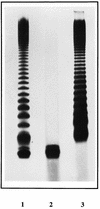
A DNA locus from Bordetella pertussis capable of reconstituting lipopolysaccharide (LPS) O-antigen biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium SL3789 (rfaF511) has been isolated, by using selection with the antibiotic novobiocin. DNA within the locus encodes a protein with amino acid sequence similarity to heptosyltransferase II, encoded by waaF (previously rfaF) in other gram-negative bacteria. Mutation of this gene in B. pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, and Bordetella bronchiseptica by allelic exchange generated bacteria with deep rough LPS phenotypes consistent with the proposed function of the gene as an inner core heptosyltransferase. These are the first LPS mutants generated in B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica and the first deep rough mutants of any of the bordetellae.
Figures


References
-
- Ackermann M R, Register K B, Gentry-Weeks C, Gwaltney S M, Magyar T. A porcine model for the evaluation of virulence of Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Comp Pathol. 1997;116:55–61. - PubMed
-
- Allen A, Maskell D. The identification, cloning and mutagenesis of a genetic locus required for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Bordetella pertussis. Mol Microbiol. 1996;19:37–52. - PubMed
-
- Amano K-I, Fukushi K, Watanabe M. Biochemical and immunological comparison of lipopolysaccharides from Bordetella species. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136:481–487. - PubMed
-
- Brooke J S, Valvano M A. Biosynthesis of inner core lipopolysaccharide in enteric bacteria identification and characterization of a conserved phosphoheptose isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:3608–3614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

