In vivo regulation of replicative Legionella pneumophila lung infection by endogenous interleukin-12
- PMID: 9423840
- PMCID: PMC107859
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.65-69.1998
In vivo regulation of replicative Legionella pneumophila lung infection by endogenous interleukin-12
Abstract
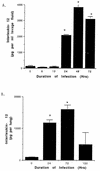
The in vivo role of endogenous interleukin 12 (IL-12) in modulating intrapulmonary growth of Legionella pneumophila was assessed by using a murine model of replicative L. pneumophila lung infection. Intratracheal inoculation of A/J mice with virulent bacteria (10(6) L. pneumophila cells per mouse) resulted in induction of IL-12, which preceded clearance of the bacteria from the lung. Inhibition of endogenous IL-12 activity, via administration of IL-12 neutralizing antiserum, resulted in enhanced intrapulmonary growth of the bacteria within 5 days postinfection (compared to untreated L. pneumophila-infected mice). Because IL-12 has previously been shown to modulate the expression of cytokines, including gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and IL-10, which regulate L. pneumophila growth, immunomodulatory effects of endogenous IL-12 on intrapulmonary levels of these cytokines during replicative L. pneumophila lung infection were subsequently assessed. Results of these experiments demonstrated that TNF-alpha activity was significantly lower, while protein levels of IFN-gamma and IL-10 in the lung were similar, in L. pneumophila-infected mice administered IL-12 antiserum, compared to similarly infected untreated mice. Together, these results demonstrate that IL-12 is critical for resolution of replicative L. pneumophila lung infection and suggest that regulation of intrapulmonary growth of L. pneumophila by endogenous IL-12 is mediated, at least in part, by TNF-alpha.
Figures

References
-
- Allendoerfer R, Boivin G P, Deepe G S., Jr Modulation of immune responses in murine pulmonary histoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:905–914. - PubMed
-
- Bamford R N, Grant A J, Burton J D, Peters C, Kurys G, Goldman C K, Brennan J, Roessler E, Waldmann T A. The interleukin (IL) 2 receptor β-chain is shared by IL-2 and a cytokine provisionally designated IL-T that stimulates T cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine activated killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:4940–4944. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertagnolli M M, Lin B Y, Young D, Herrmann S H. IL-12 augments antigen-dependent proliferation of activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992;149:3778–3783. - PubMed
-
- Biron C A, Gazzinelli R T. Effects of IL-12 on immune responses to microbial infections: a key mediator in regulating disease outcome. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:485–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

