Distinct characteristics of resistance to Borrelia burgdorferi-induced arthritis in C57BL/6N mice
- PMID: 9423853
- PMCID: PMC107872
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.161-168.1998
Distinct characteristics of resistance to Borrelia burgdorferi-induced arthritis in C57BL/6N mice
Abstract
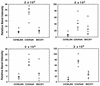
Studies of mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi have indicated that the severity of arthritis is influenced by the genetic composition of the host: the C3H mouse develops severe arthritis while BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice develop mild arthritis. In this study, the effects of increasing infectious dose on the severity of arthritis were determined in these three mouse strains. C3H/He mice developed severe arthritis at all infectious doses, with 100% infection requiring 200 spirochetes. In BALB/cAnN mice, arthritis severity was dependent on infectious dose; symptoms were mild with infection by 200 B. burgdorferi and progressively more severe with increasing infectious dose. Infection of BALB/cAnN mice with 2 x 10(4) B. burgdorferi resulted in arthritis with severity identical to that in C3H/He mice. Spirochete levels in rear ankle joints of C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeN mice were relatively high, as detected by PCR, and did not increase with infectious dose. Spirochete levels in joints from BALB/cAnN mice increased with increasing infectious dose to levels found in severely arthritic C3H/He mice. Thus, resistance to severe arthritis in BALB/cAnN mice was conditional: it could be overcome by high infectious dose and the arthritis became severe when high levels of B. burgdorferi were present in joints. A unique response to increasing infectious dose was seen in C57BL/6N mice, which displayed mild to moderate arthritis at all doses of B. burgdorferi tested, up to 2 x 10(5). At all infectious doses, the levels of spirochetes in ankle joints of C57BL/6N mice were high, equivalent to those found in the severely arthritic C3H/He mice. The arthritis observed in infected (C57BL/6N x C3H/HeN)F1 mice was of severity intermediate between those of the two parental strains. The finding that resistance to severe arthritis in C57BL/6N mice could not be overcome by high infectious doses and was independent of spirochete levels in joints suggested that it was mediated by a distinct mechanism from that operating in BALB/cAnN mice.
Figures
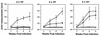





References
-
- Akins D R, Porcella S F, Popova T G, Shevchenko D, Baker S I, Li M, Norgard M V, Radolf J D. Evidence for in vivo but not in vitro expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein F (OspF) homologue. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:507–520. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong A L, Barthold S W, Persing D H, Beck D S. Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;47:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Balmelli T, Piffaretti J C. Association between different clinical manifestations of Lyme disease and different species of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. Res Microbiol. 1995;146:329–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

