Modulation of murine Lyme borreliosis by interruption of the B7/CD28 T-cell costimulatory pathway
- PMID: 9423867
- PMCID: PMC107886
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.266-271.1998
Modulation of murine Lyme borreliosis by interruption of the B7/CD28 T-cell costimulatory pathway
Abstract
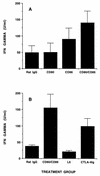
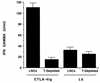
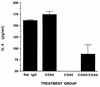
Recent studies have implicated cytokines associated with Th2 cells in the genetic resistance to murine Lyme borreliosis. Because the B7/CD28 costimulatory pathway has been shown to influence the differentiation of Th-cell subsets, we investigated the contribution of the B7 molecules CD80 and CD86 to the Th2 cytokine profile and development of arthritis in BALB/c mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Effective blockade of CD86/CD28 interaction was demonstrated by elimination of interleukin 4 (IL-4) and upregulation of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) responses by B. burgdorferi-specific T cells and by reduction of B. burgdorferi-specific immunoglobulin G. Despite the shift toward a Th1 cytokine pattern, which others have associated with disease susceptibility, the severity of arthritis was unchanged. Moreover, combined CD80/CD86 blockade by using anti-CD80 and anti-CD86 monoclonal antibodies or CTLA-4Ig enhanced IFN-gamma production over that seen with CD86 blockade alone, yet augmentation of this Th1-associated cytokine did not enhance disease. These results demonstrate that IL-4 production by T cells in B. burgdorferi-infected BALB/c mice is dependent upon CD86/CD28 interaction and that this cytokine does not contribute significantly to host resistance to the development of arthritis. In addition, combined CD80/CD86 blockade resulted in preferential expansion of IFN-gamma-producing T cells in B. burgdorferi infection, suggesting that costimulatory pathways other than B7/CD28 may contribute to T-cell activation during continuous antigen stimulation. These studies may provide insight into the role of the B7/CD28 pathway in other infectious and autoimmune diseases in which deviation of Th cell immune responses occurs and antigen is persistently present.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of experimental blood stage malaria through blockade of the B7/CD28 T-cell costimulatory pathway.Immunology. 1999 Mar;96(3):498-504. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00718.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10233733 Free PMC article.
-
Costimulation light: activation of CD4+ T cells with CD80 or CD86 rather than anti-CD28 leads to a Th2 cytokine profile.J Immunol. 2000 Dec 15;165(12):6908-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.6908. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11120816
-
CD80 expression is induced on activated B cells following stimulation by CD86.Scand J Immunol. 2002 Jun;55(6):577-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2002.01093.x. Scand J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12028560
-
Role of B7 signaling in the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells to effector interleukin-4-producing T helper cells.Immunol Res. 1995;14(3):176-88. doi: 10.1007/BF02918215. Immunol Res. 1995. PMID: 8778208 Review.
-
Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.225. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244036 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 signaling pathways do not regulate Borrelia burgdorferi-induced arthritis in mice: IgG1 is not required for host control of tissue spirochetes.Infect Immun. 2000 Oct;68(10):5603-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5603-5609.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10992460 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T helper 1 cells facilitate regression of murine Lyme carditis.Infect Immun. 2001 Sep;69(9):5264-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5264-5269.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11500394 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral immunity reflects altered T helper cell bias in Borrelia burgdorferi-infected gamma delta T-cell-deficient mice.Infect Immun. 2003 May;71(5):2938-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2938-2940.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12704174 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-12 neutralization alters lung inflammation and leukocyte expression of CD80, CD86, and major histocompatibility complex class II in mice infected with Histoplasma capsulatum.Infect Immun. 2000 Apr;68(4):2069-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.2069-2076.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10722603 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role for type I IFN in arthritis development following Borrelia burgdorferi infection of mice.J Immunol. 2008 Dec 15;181(12):8492-503. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8492. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19050267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barthold S W, Beck D S, Hansen G M, Terwilliger G A, Moody K D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990;162:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Barthold, S. W., S. Feng, L. K. Bockenstedt, E. Fikrig, and K. Feen. 1997. Protective and arthritis-resolving activity in serum of mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 25(Suppl. 1):S9–S17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

