Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in endophthalmitis
- PMID: 9423880
- PMCID: PMC107899
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.356-360.1998
Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in endophthalmitis
Abstract
Genomic DNA fingerprint analysis was performed on 39 Staphylococcus aureus and 28 Enterococcus faecalis endophthalmitis isolates collected from multiple clinical centers. Among 21 S. aureus genomic DNA fingerprint patterns identified, five clonotypes were recovered from multiple unrelated patients and accounted for 58.9% (23 of 39) of the isolates analyzed. Compared with strains having unique genomic DNA fingerprint patterns, the S. aureus clonotypes occurring more than once were more likely to result in visual acuities of 20/200 or worse (P = 0.036 [chi2 test]). In contrast to the S. aureus isolates, the E. faecalis endophthalmitis isolates were a clonally diverse population, enriched for the expression of a known toxin, cytolysin, which is plasmid encoded.
Figures
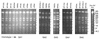
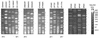
References
-
- Affeldt J C, Flynn H W, Forster R K, Mandelbaum S, Clarkson J G, Jarus G D. Microbial endophthalmitis resulting from ocular trauma. Ophthalmology. 1987;94:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman T L, Rhoden D L, McAllister S K, Miller J M, Wilson L A. The source of coagulase negative staphylococci in the endophthalmitis vitrectomy study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115:357–361. - PubMed
-
- Booth M C, Atkuri R V, Nanda S K, Iandolo J J, Gilmore M S. Accessory gene regulator controls Staphylococcus aureus virulence in endophthalmitis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995;36:1828–1836. - PubMed
-
- Brinton G S, Topping T M, Hyndiuk R A, Aaberg T M, Reeser F H, Abrams G W. Posttraumatic endophthalmitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:547–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

