Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children
- PMID: 9430746
- PMCID: PMC5075245
- DOI: 10.1044/jslhr.4006.1245
Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children
Abstract
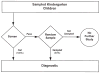
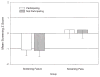
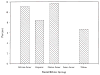
This epidemiologic study estimated the prevalence of specific language impairment (SLI) in monolingual English-speaking kindergarten children. From a stratified cluster sample in rural, urban, and suburban areas in the upper midwest, 7,218 children were screened. The language screening failure rate was 26.2%. Children who failed the screening and a similar number of controls were then administered a diagnostic battery (n = 2,084) that provided for a diagnosis of SLI using common diagnostic standards. Results provided an estimated overall prevalence rate of 7.4%. The prevalence estimate for boys was 8% and for girls 6%. Variation in prevalence was found among children of different racial/cultural backgrounds; however, these background variables were found to be correlated with parental education, which was also associated with SLI. The parents of 29% of the children identified as SLI reported they had previously been informed that their child had a speech or language problem. The prevalence estimates obtained fell within recent estimates for SLI, but demonstrated that this condition is more prevalent among females than has been previously reported. Also, the clinical identification of these children remains low among kindergarteners.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Aram DM, Morris R, Hall NE. Clinical and research congruence in identifying children with specific language impairment. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1993;36:580–591. - PubMed
-
- Bangs TE. Language and learning disorders of the pre-academic child. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1968.
-
- Beitchman JH, Nair R, Clegg M, Patel PG. Prevalence of speech and language disorders in 5-year-old kindergarten children in the Ottawa-Carleton region. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders. 1986;51:98–110. - PubMed
-
- Beitchman JH, Nair R, Clegg M, Ferguson B. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in children with speech and language disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry. 1986;25:528–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

