Identification of streptococci to species level by sequencing the gene encoding the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase
- PMID: 9431917
- PMCID: PMC124804
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.1.41-47.1998
Identification of streptococci to species level by sequencing the gene encoding the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase
Abstract
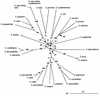
We have used a PCR assay based on the use of degenerate primers in order to characterize an internal fragment (sodA(int)) representing approximately 85% of the genes encoding the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase in various streptococcal type strains (S. acidominimus, S. agalactiae, S. alactolyticus, S. anginosus, S. bovis, S. constellatus, S. canis, S. cricetus, S. downei, S. dysgalactiae, S. equi subsp. equi, S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus, S. equinus, S. gordonii, S. iniae, S. intermedius, S. mitis, S. mutans, S. oralis, S. parasanguis, S. pneumoniae, S. porcinus, S. pyogenes, S. salivarius, S. sanguis, S. sobrinus, S. suis, S. thermophilus, and S. vestibularis). Phylogenetic analysis of these sodA(int) fragments yields an evolutionary tree having a topology similar to that of the tree constructed with the 16S rRNA sequences. We have shown that clinical isolates could be identified by determining the positions of their sodA(int) fragments on the phylogenetic tree of the sodA(int) fragments of the type species. We propose this method for the characterization of strains that cannot be assigned to a species on the basis of their conventional phenotypic reactions.
Figures


References
-
- Adnan S, Li N, Miura H, Hashimoto Y, Yamamoto H, Ezaki T. Covalently immobilized DNA plate for luminometric DNA-DNA hybridization to identify viridans streptococci in under 2 hours. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993;106:139–142. - PubMed
-
- Beighton D, Hardie J M, Whiley A. A scheme for the identification of viridans streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1991;35:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Bentley R W, Leigh J A, Collins M D. Intrageneric structure of Streptococcus based on comparative analysis of small-subunit rRNA sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991;41:487–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

