Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activity in CD40 signaling along a ras-independent pathway
- PMID: 9432981
- PMCID: PMC2212104
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.2.237
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activity in CD40 signaling along a ras-independent pathway
Abstract
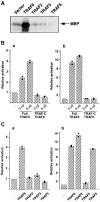
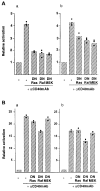
CD40 activates nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) subfamily, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). The CD40 cytoplasmic tail interacts with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)2, TRAF3, TRAF5, and TRAF6. These TRAF proteins, with the exception of TRAF3, are required for NF kappa B activation. Here we report that transient expression of TRAF6 stimulated both ERK and NF kappa B activity in the 293 cell line. Coexpression of the dominant-negative H-Ras did not affect TRAF6-mediated ERK activity, suggesting that TRAF6 may activate ERK along a Ras-independent pathway. The deletion mutant of TRAF6 lacking the NH2-terminal domain acted as a dominant-negative mutant to suppress ERK activation by full-length CD40 and suppress prominently ERK activation by a deletion mutant of CD40 only containing the binding site for TRAF6 in the cytoplasmic tail (CD40 delta 246). Transient expression of the dominant-negative H-Ras significantly suppressed ERK activation by full-length CD40, but marginally suppressed ERK activation by CD40 delta 246, compatible with the possibility that TRAF6 is a major transducer of ERK activation by CD40 delta 246, whose activity is mediated by a Ras-independent pathway. These results suggest that CD40 activates ERK by both a Ras-dependent pathway and a Ras-independent pathway in which TRAF6 could be involved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential requirements for tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family proteins in CD40-mediated induction of NF-kappaB and Jun N-terminal kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 6;274(32):22414-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.32.22414. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10428814
-
CD40 signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Binding site specificity and activation of downstream pathways by distinct TRAFs.J Biol Chem. 1999 May 14;274(20):14246-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.20.14246. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10318845
-
Characterization of the roles of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 in CD40-mediated B lymphocyte effector functions.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):623-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.623. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10623803
-
Roles of TRAF6 in CD40 signaling.Immunol Res. 2007;39(1-3):105-14. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0082-3. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917059 Review.
-
CD40-CD154 interactions in B-cell signaling.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;245(2):73-99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59641-4_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10533319 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Exosome-delivered miR-410-3p reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of trophoblasts in spontaneous abortion.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Feb;28(3):e18097. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18097. Epub 2024 Jan 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38164738 Free PMC article.
-
p53 Ubiquitination Comediated by HUWE1 and TRAF6 Contributes to White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection in Crustacean.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0202921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02029-21. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35107378 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 induces apoptosis in carcinoma cells through activation of cytotoxic ligands of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;20(15):5503-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.15.5503-5515.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891490 Free PMC article.
-
β-Boswellic Acid Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation and Function by Attenuating NF-κB and Btk-PLCγ2 Signaling Pathways.Molecules. 2021 May 1;26(9):2665. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092665. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34062884 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal role of ERK and NF-kappaB pathways in survival and activation of osteoclasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jan 24;148(2):333-42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.2.333. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banchereau J, Bazan F, Blanchard D, Briere F, Galizzi JP, van Kooten C, Liu YJ, Rousset F, Saeland S. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. - PubMed
-
- Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1994;78:681–692. - PubMed
-
- Hu HM, O'Rourke K, Boguski MS, Dixit VM. A novel RING finger protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD40. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30069–30072. - PubMed
-
- Sato T, Irie S, Reed JC. A novel member of the TRAF family of putative signal transducing proteins binds to the cytosolic domain of CD40. FEBS Lett. 1995;358:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Cleary AM, Ye ZS, Hong DI, Lederman S, Baltimore D. Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science. 1995;267:1494–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

