The importance of tRNA backbone-mediated interactions with synthetase for aminoacylation
- PMID: 9435214
- PMCID: PMC18442
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.460
The importance of tRNA backbone-mediated interactions with synthetase for aminoacylation
Abstract
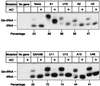
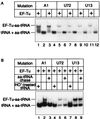
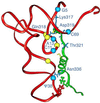
We have identified six new aminoacylation determinants of Escherichia coli tRNAGln in a genetic and biochemical analysis of suppressor tRNA. The new determinants occupy the interior of the acceptor stem, the inside corner of the L shape, and the anticodon loop of the molecule. They supplement the primary determinants located in the anticodon and acceptor end of tRNAGln described previously. Remarkably, the three-dimensional structure of the complex between tRNAGln and glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase shows that the enzyme interacts with the phosphate-sugar backbone but not the base of every new determinant. Moreover, a small protein motif interacts with five of these determinants, and it binds proximal to the sixth. The motif also interacts with the middle base of the anticodon and with the backbones of six other nucleotides. Our results emphasize that synthetase recognition of tRNA is more elaborate than amino acid side chains of the enzyme interacting with nucleotide bases of the tRNA. Recognition also includes synthetase interaction with tRNA backbone functionalities whose distinctive locations in three-dimensional space are exquisitely determined by the tRNA sequence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution.Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135-42. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. Science. 1989. PMID: 2479982
-
Functional connectivity between tRNA binding domains in glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase.J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 15;256(5):818-28. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0128. J Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8601833
-
Association of tRNA(Gln) acceptor identity with phosphate-sugar backbone interactions observed in the crystal structure of the Escherichia coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase-tRNA(Gln) complex.Biochimie. 1993;75(12):1125-36. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90012-h. Biochimie. 1993. PMID: 8199248
-
Selectivity and specificity in the recognition of tRNA by E coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase.Biochimie. 1993;75(12):1083-90. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90007-f. Biochimie. 1993. PMID: 8199243 Review.
-
Mutant enzymes and tRNAs as probes of the glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase: tRNA(Gln) interaction.Biochimie. 1991 Dec;73(12):1501-8. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90184-3. Biochimie. 1991. PMID: 1725262 Review.
Cited by
-
A sequence element that tunes Escherichia coli tRNA(Ala)(GGC) to ensure accurate decoding.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Apr;16(4):359-64. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1581. Epub 2009 Mar 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19305403 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of acceptor-stem structure of tRNA(Asp) by Escherichia coli aspartyl-tRNA synthetase.RNA. 2003 Apr;9(4):386-93. doi: 10.1261/rna.2139703. RNA. 2003. PMID: 12649491 Free PMC article.
-
Improved amber and opal suppressor tRNAs for incorporation of unnatural amino acids in vivo. Part 1: minimizing misacylation.RNA. 2007 Oct;13(10):1703-14. doi: 10.1261/rna.666807. Epub 2007 Aug 13. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17698638 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of 2'-hydroxyl and phosphate groups important for aminoacylation of Escherichia coli tRNAAsp: a nucleotide analogue interference study.RNA. 1998 Nov;4(11):1444-54. doi: 10.1017/s1355838298980967. RNA. 1998. PMID: 9814764 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of deformability at a tRNA recognition site and aminoacylation specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Oct 12;96(21):11764-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.11764. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10518524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnez J G, Moras D. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:211–216. - PubMed
-
- Rould M A, Perona J J, Söll D, Steitz T A. Science. 1989;246:1135–1142. - PubMed
-
- Ruff M, Krishnaswamy S, Boeglin M, Poterszman A, Mitschler A, Podjarny A, Rees B, Thierry J C, Moras D. Science. 1991;252:1682–1689. - PubMed
-
- Biou V, Yaremchuk A, Tukalo M, Cusack S. Science. 1994;263:1404–1410. - PubMed
-
- Goldgur Y, Mosyak L, Reshetnikova L, Ankilova V, Lavrik O, Khodyreva S, Safro M. Structure. 1997;5:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

